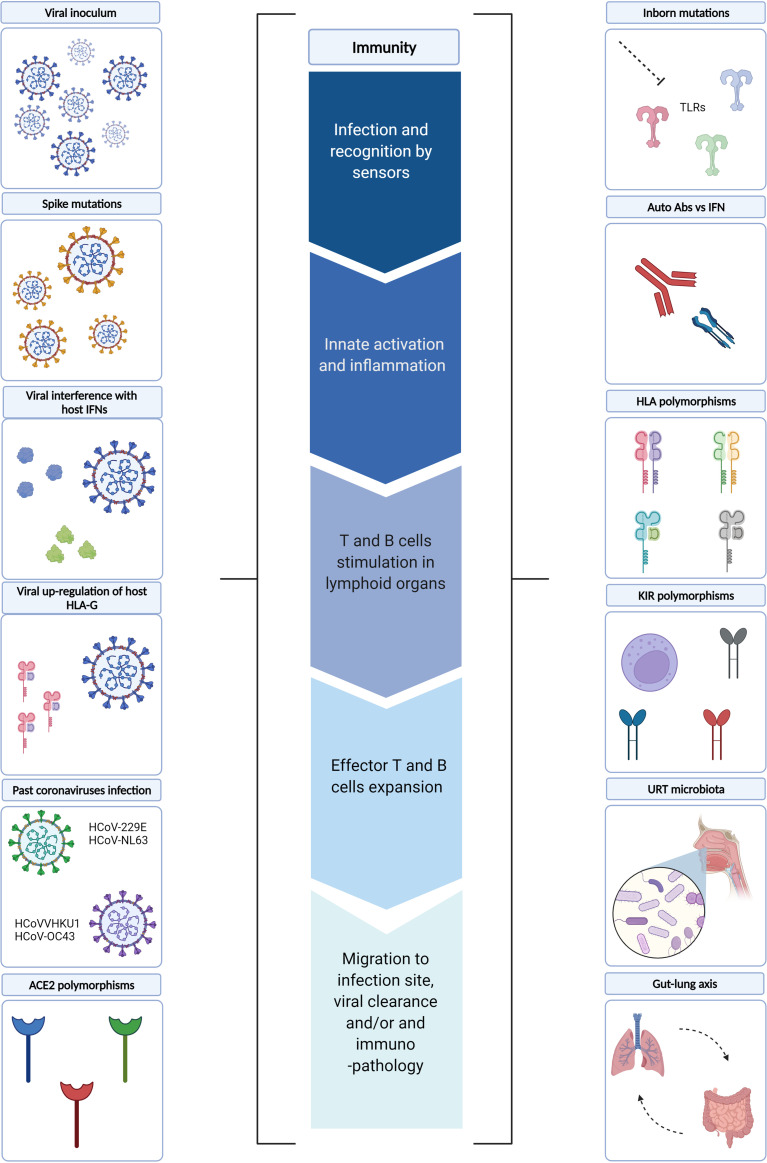
Figure 2.
Underlying mechanisms of immune dysregulation. Several viral and host factors have been described as influencing one or more steps of the immune response during SARS-CoV-2 infection. In particular, the early phases of the immune response may be influenced by i) viral factors, such as viral inoculum, Spike mutations and viral interference of host IFN pathways, as well as ii) host factors, such as ACE2 polymorphisms and URT microbiota. Whereas viral up-regulation of host HLA-G, inborn host mutations, auto-reactive Abs vs IFN, HLA and KIR polymorphisms, past coronavirus infections may influence the later phases of immune responses. In this context, gut-lung axis perturbations may further fuel systemic inflammation. TLRs, Toll-like receptors; IFN, Interferon; Abs: Antibodies; HLA, Human Leukocyte Antigens; KIRs, Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptors; URT, Upper Respiratory Tract; ACE2, Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2. Created with BioRender.com.