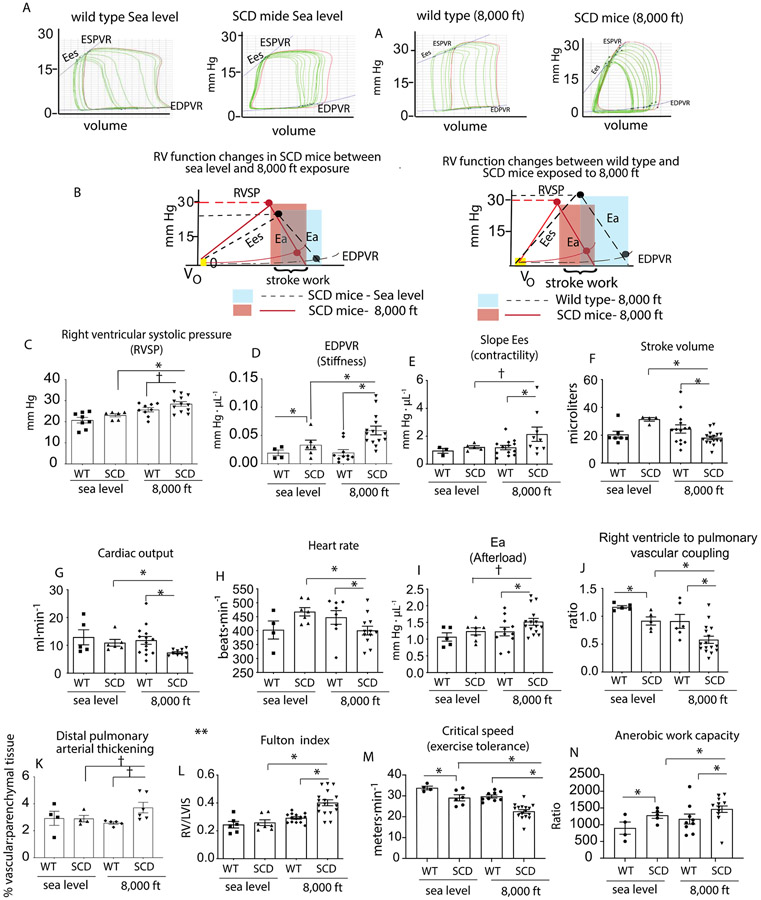
Figure 4: SCD mice housed for 3 months at moderate hypoxia (8,000 ft) demonstrate progressive pulmonary vascular disease.
(A) Representative tracings of pressure volume (PV) loops during an occlusion for wild type and SCD mice housed at either sea level or moderate hypoxia (8,000 ft) (B) shows the corresponding schematics of the pressure volume relationships for wild type and SCD mice for each cohort. (C-J) Right ventricular functional analysis in wild type and SCD mice showing right ventricular systolic pressure, stiffness, contractility, stroke volume, cardiac output, heart rate, afterload and right ventricle to pulmonary vascular coupling ratio. (K) Pulmonary vascular thickening (L) right ventricular hypertrophy. (M) Critical speed. (N) Anerobic work capacity. Data is represented as means ± standard error of measurement. RVSP- right ventricular pressures; Ea-Afterload; EDPVR-end diastolic pressure volume relationship; ESPVR- end systolic pressure volume relationship. *p<0.05 vs. SCD mice at 8,000 ft; † p < 0.05 vs SCD mice t-test