Fig 1. Biochemical and machine learning workflow diagrams.
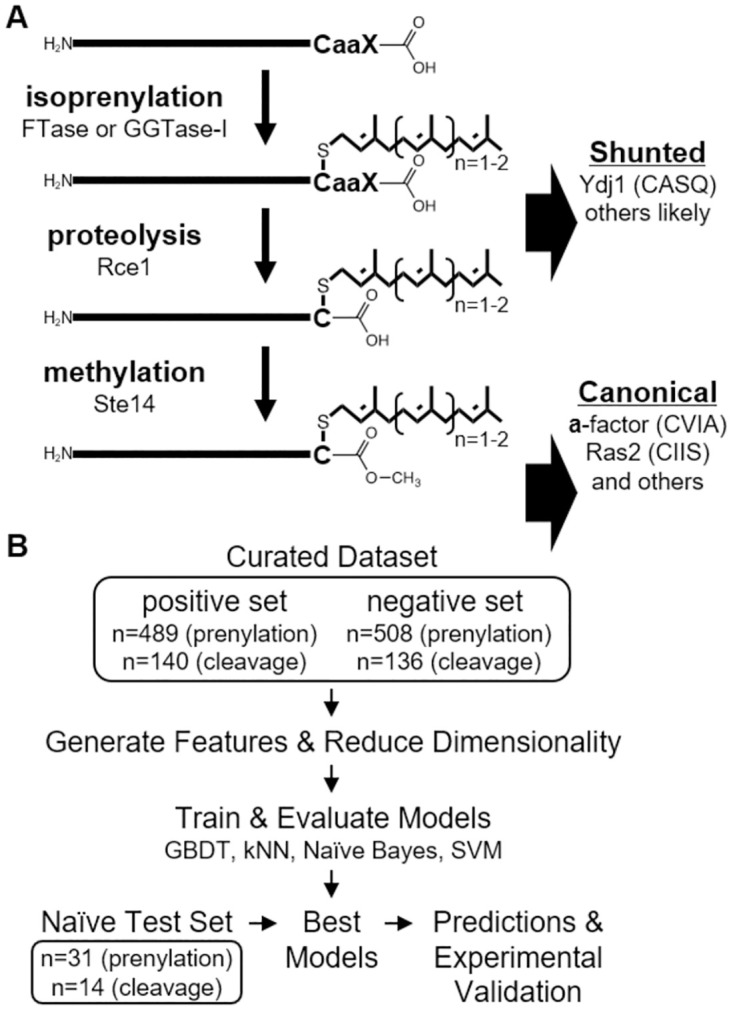
A) Modifications occurring to CAAX proteins. Isoprenylation involves attachment of a farnesyl (C15) or geranylgeranyl (C20) lipid to the consensus cysteine amino acid (C) of a COOH-terminal CaaX motif. Shunted CaaX proteins are not further modified. Canonical CaaX proteins undergo proteolytic cleavage to remove the ‘aaX’ portion of the motif and carboxylmethylation of the isoprenylated cysteine. Examples shown are yeast proteins, but examples exist in other systems. a–aliphatic amino acid; X–one of several amino acids. B) Positive and negative training sets for prenylation and cleavage predictions were curated from published data, used to generate features, then used to train four machine learning algorithms. The trained models were subject to 10-fold cross validation to determine accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. The best models, along with a PSSM-based model, were then used to predict prenylation and cleavage outcomes for naïve test sequences that were compared against the experimental observed properties of these sequences.
