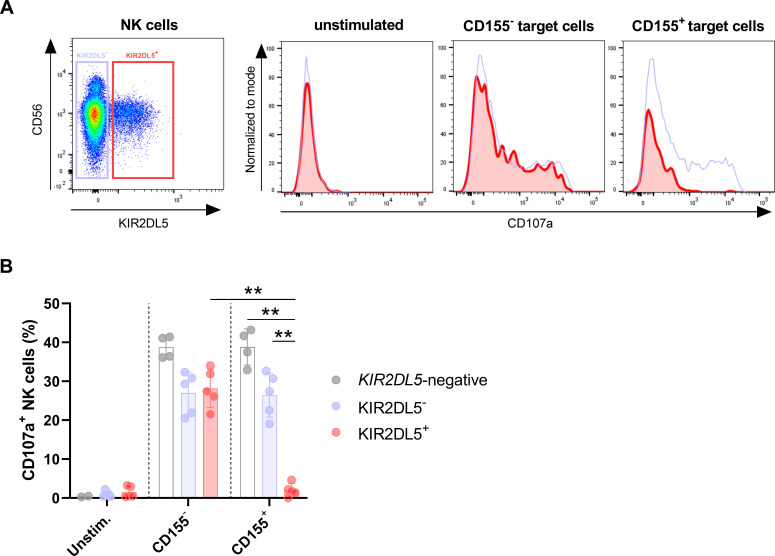
Fig 3. Primary human KIR2DL5+ NK cells are inhibited by CD155-expressing target cells.
(A) Degranulation of KIR2DL5+ (red) and KIR2DL5- (blue) NK cells was defined as percentage of CD107a+ NK cells after co-incubation with CD155- 721.221 target cells, CD155+ 721.221 target cells or left unstimulated. Plots show one representative experiment out of five independent experiments. (B) Percentage of CD107a-positive NK cells after co-incubation with target cells is shown as indicated before. Bars indicate mean values with standard deviations of KIR2DL5+ donors (n = 5 from 5 donors) and KIR2DL5-negative donors (n = 4 from 2 donors). Mann-Whitney test was used to calculate statistical significance of differences in CD107a levels (KIR2DL5- versus KIR2DL5+ NK cells p = 0.008; KIR2DL5-negative versus KIR2DL5+ NK cells p = 0.016; KIR2DL5+ NK cells co-cultured with CD155+ or CD155- target cells p = 0.008).