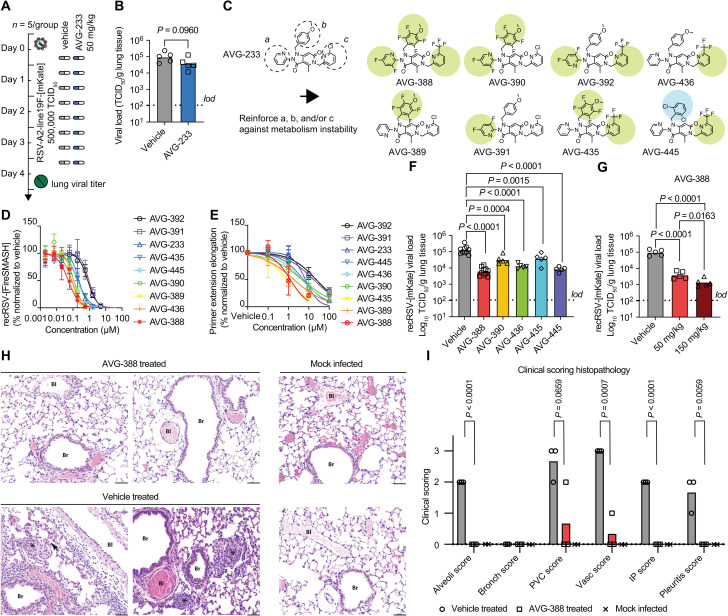
Fig. 5. Identification of orally efficacious developmental analogs of AVG-233.
(A and B) Effect of AVG-233 given orally twice daily at 12 hours postinfection (A) to RSV-infected Balb/c mice on lung titers at 4.5 d.p.i. (B). (C) Chemical structures of AVG-233 analogs with fluoro- or ortho-chloropyridine groups. (D and E) Comparison of AVG fluorine and ortho-chloropyridine analogs on antiviral potency in cell culture against recRSV-mKate (D) and in in vitro primer extension RdRP assays (E). (F and G) Effect of AVG-233 analogs given orally twice daily at 12 hours postinfection and 50 mg/kg (F) or 50 and150 mg/kg (G; AVG-388 only) to recRSV-mKate–infected Balb/cJ mice on lung titers at 4.5 d.p.i. (H and I) Lung histopathology. Representative photomicrographs of lung sections after H&E staining of two animals per treatment group (H) and histopathology scoring (I; n = 3 each for AVG-388– and vehicle-treated groups, n = 2 for mock-infected group). Bl, blood vessel; Br, bronchiole; arrow, interstitial pneumonia; asterisks, alveolitis. Scale bars, 50 μm. The histopathology scoring scale applied is defined in Materials and Methods. Symbols in (B), (F), (G), and (I) show individual biological repeats (independent experiments or individual animals); columns represent sample means. Unpaired t test (B) or one-way ANOVA (F, G, and I) with Dunnett’s (F and G) or Tukey’s (I) multiple comparisons post hoc test; P values are shown.