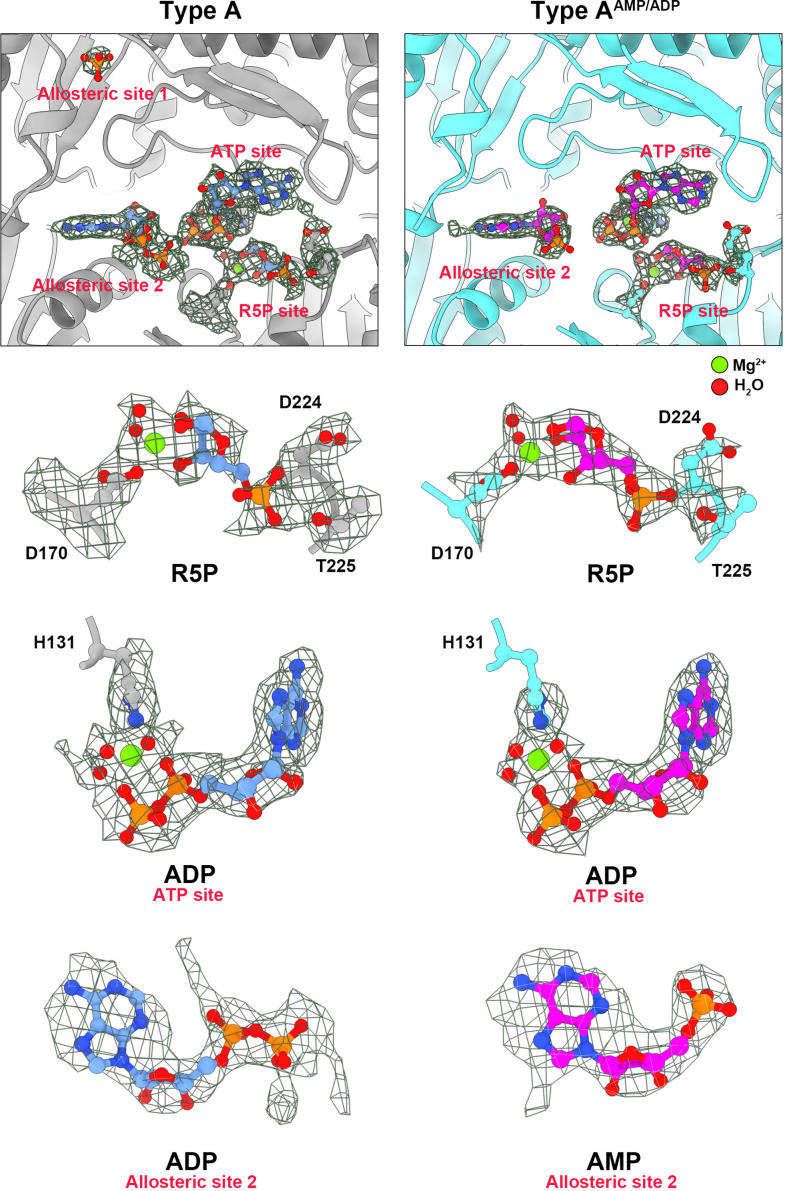
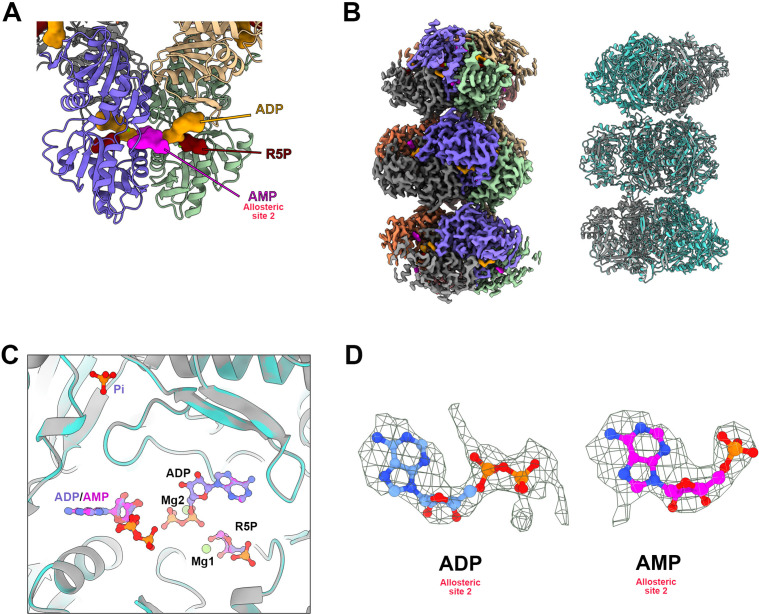
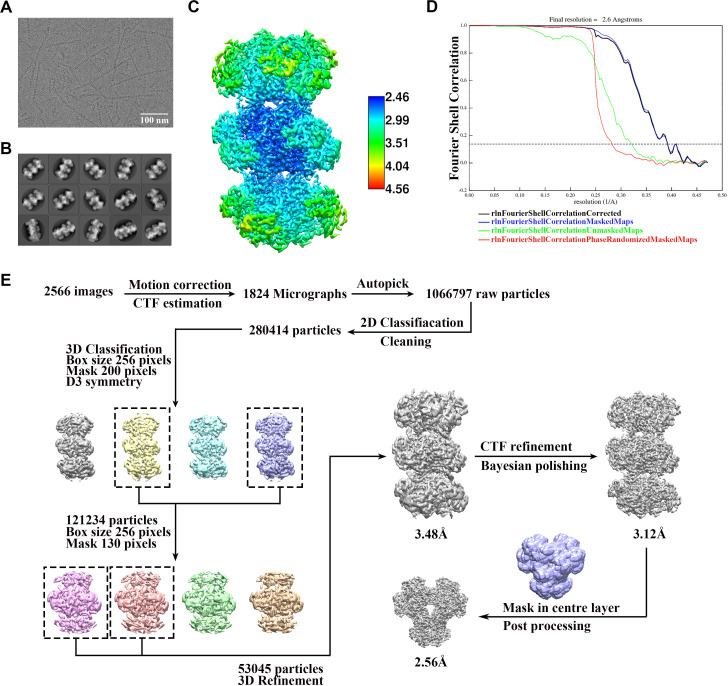
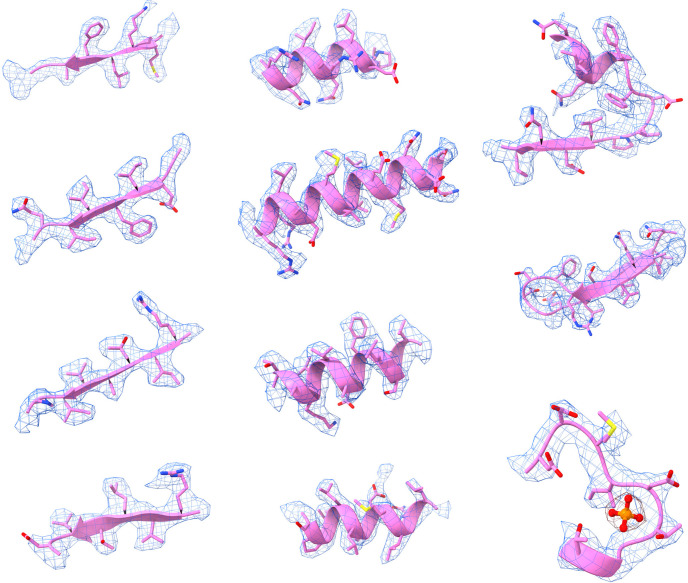
Figure 1. with 8 supplements.
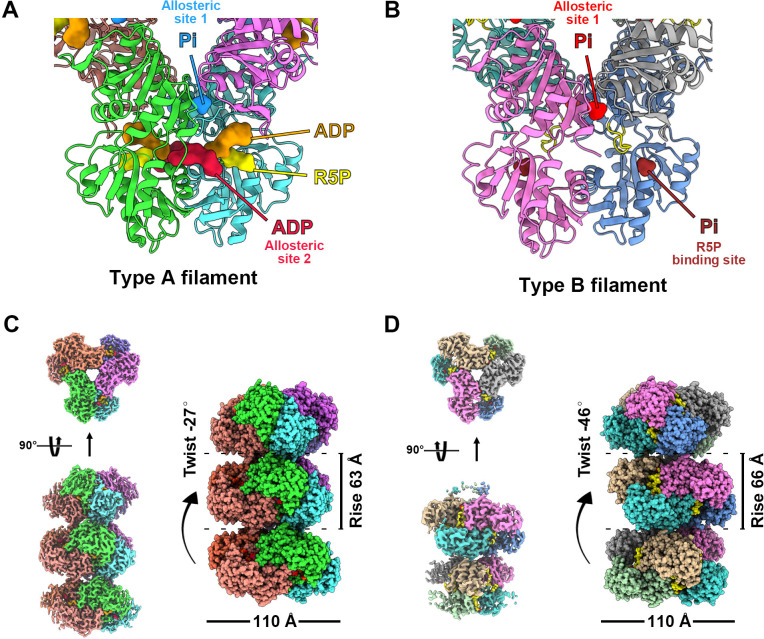
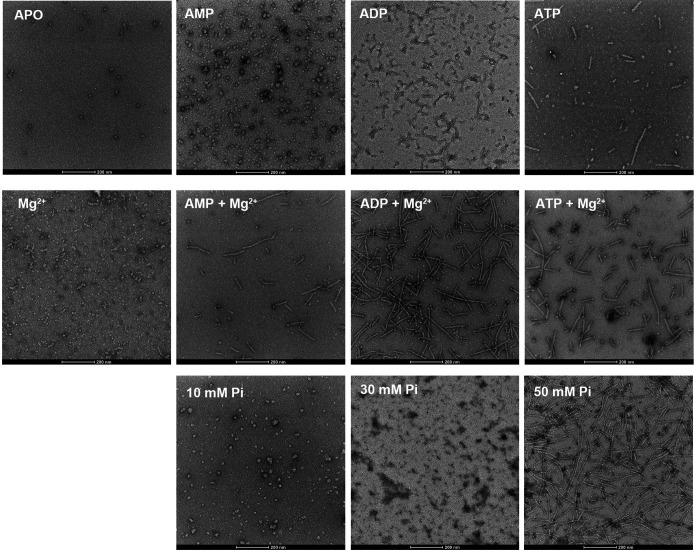
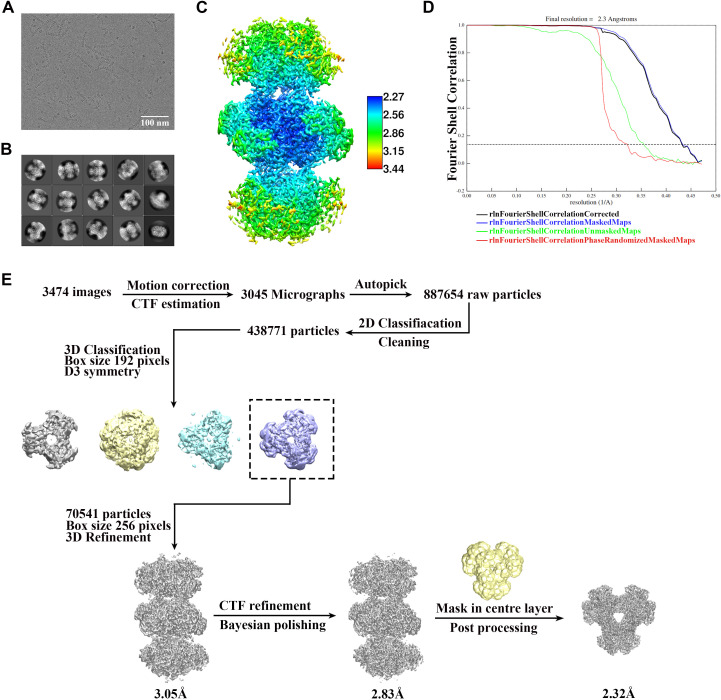
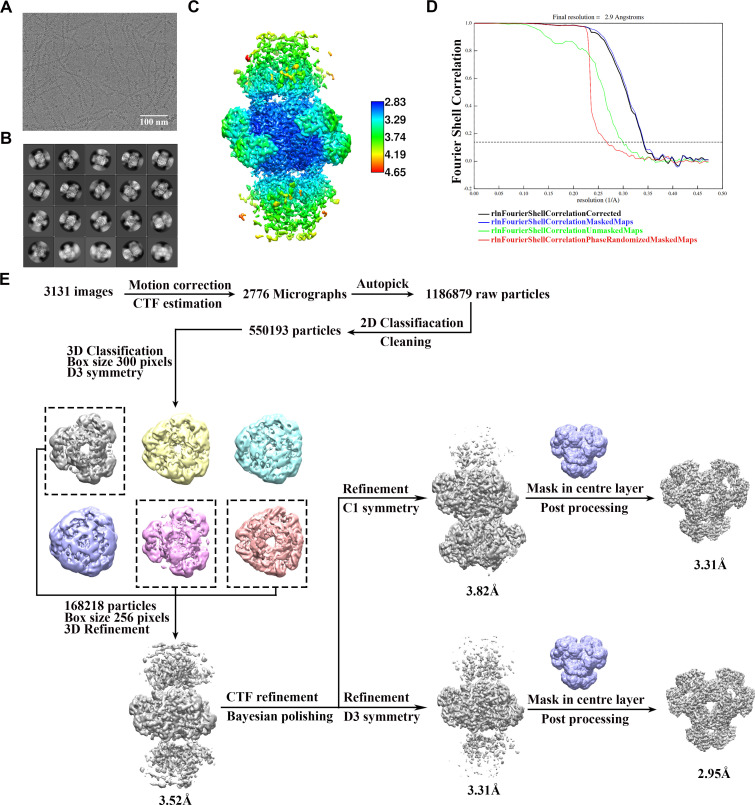
Overall structures of E. coli PRPS type A and type B filaments. (A) Type A filament ligands. The unit of E. coli PRPS type A filaments is hexamer with D3 symmetry. The hexamer has six identical ligand binding sites, one of which is shown in the figure. Different ligands are labeled with different colors. In type A filament, phosphate ion (Pi) binds to allosteric site 1, ADP binds to allosteric site 2 (red), and ATP binds to active site (brown). R5P also can be seen in the active site. (B) Type B filament ligands. The unit of type B filament is similar to that of type A filament, and one of the six identical ligand binding sites is shown here. In type B filament, the ATP binding site of active site is not bound by any ligand, while the R5P binding site and allosteric site 1 are bound by Pi. (C) Cryo-EM reconstruction of type A filament (C, 2.3 Å resolution). On the left is the electron density map of type A filament. On the right is the reconstruction structure of type A filament. The diameter and rise of type A filament are 110 Å and 63 Å, respectively. When hexamers are aggregated into type A filament, the adjacent hexamer us twisted by 27°. (D) Cryo-EM reconstructions of type B filament (2.9 Å resolution). On the left is electron density map of type A filament. On the right is the reconstruction structure of type A filament. The diameter of type B filament is same as that of type A filament. The rise and twist of type B filament are 66 Å and 46°, respectively.