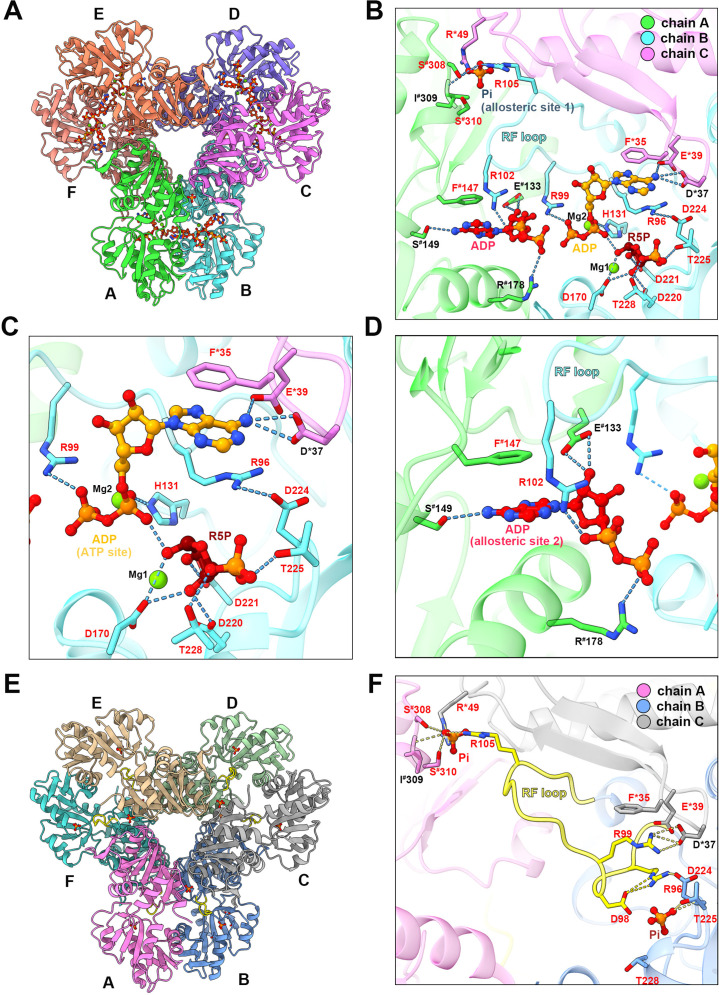
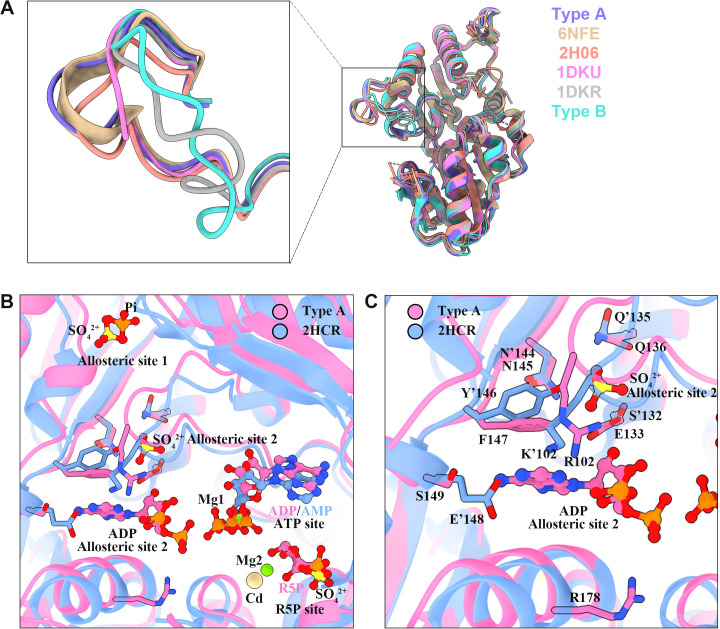
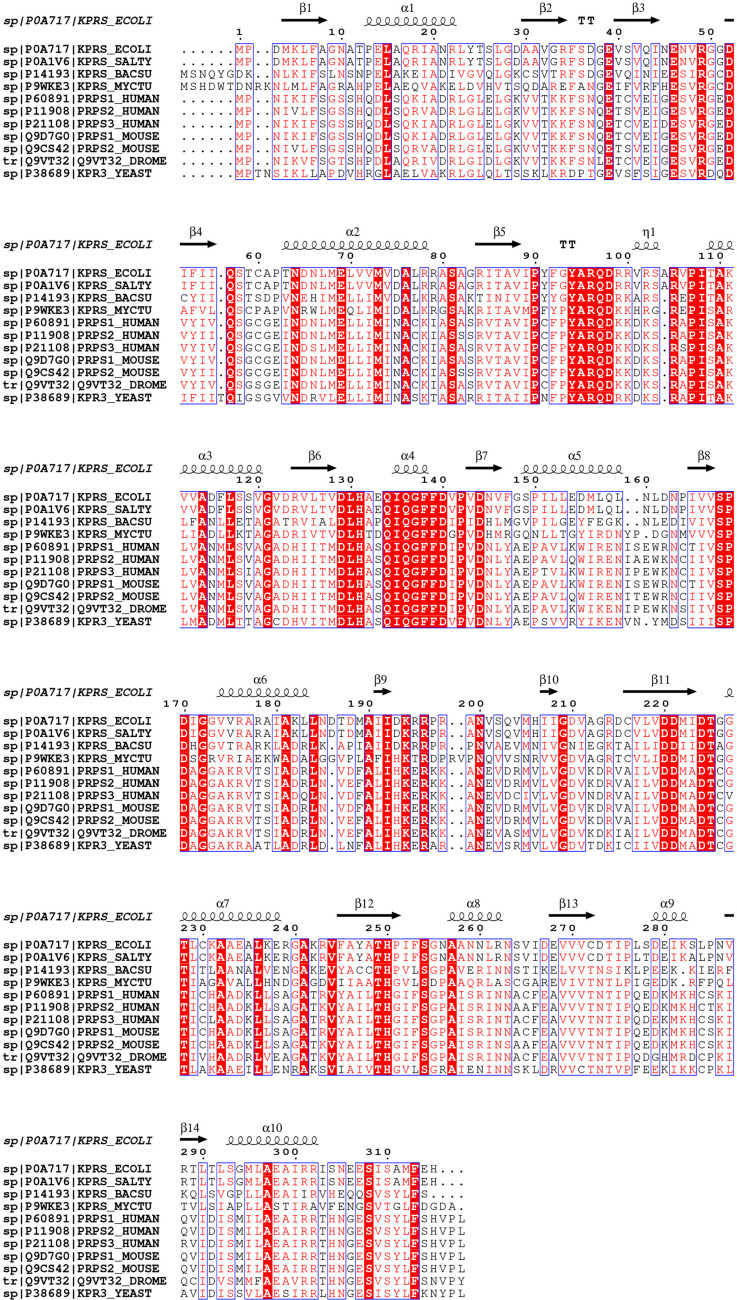
Figure 3. with 2 supplements.
Ligand binding modes in E. coli PRPS type A and type B filaments. (A) Hexamer of type A filament. Each chain is marked with a different color. (B) ADP and R5P are identified on the active site of PRPS in type A filament, while allosteric site 1 is bound by Pi and allosteric site 2 is bound by ADP. The residues that interact with ligands are indicated. Residues in chain A number with the # symbol and in chain C number with the * symbol. Residues in red are conserved in various organisms. Each chain is marked with a different color(dash lines in cyan indicate hydrogen bonds). (C) Ligands of the active site of type A filament. ADP and Mg2+ occupy ATP binding sites at active sites. R5P and Mg2+ can also be seen in the active site. Residues in red are conserved in various organisms. Each chain is marked with a different color. (D) ADP in allosteric site 2 of type A filament. Residues in red are conserved in various organisms. Each chain is marked with a different color. (E) Hexamer of type B filament. Each chain is marked with a different color. (F) In type B filament, the ATP binding site of the active site is not bound by any ligand, while the R5P binding site and allosteric site 1 are bound by Pi. Residues in chain A number with the # symbol and in chain C number with the * symbol. Residues in red are conserved in various organisms. Each chain is marked with a different color(dash lines in yellow indicate hydrogen bonds).