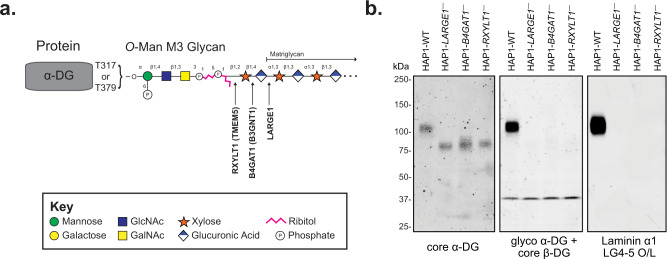
Fig. 1. Functional Glycosylation of α-Dystroglycan.
a Cartoon representation of the fully elaborated O-mannose M3 glycan that is present on 2 sites of α-dystroglycan with the three post-ribitol enzymes needed for priming and synthesis of matriglycan shown. Carbohydrate symbol representation is consistent with Symbol Nomenclature for Graphical Representations of Glycans71. b Endogenous α-DG was examined in human HAP1 cells (HAP1-WT) as well as HAP1 cells with genetic defects in the post-ribitol enzymes RXYLT1, B4GAT1, or LARGE1. The molecular weight of α-DG was greatly diminished in the cells lacking the post-ribitol glycosyltransferases and was no longer reactive with the IIH6 antibody. α-DG from the three cell lines lacking these enzymes also displayed a complete loss of binding to laminin in an overlay assay. These results highlight the importance of post-ribitol glycosyltransferases for functional glycosylation of α-DG. Three independent experiments were performed with similar results each time.