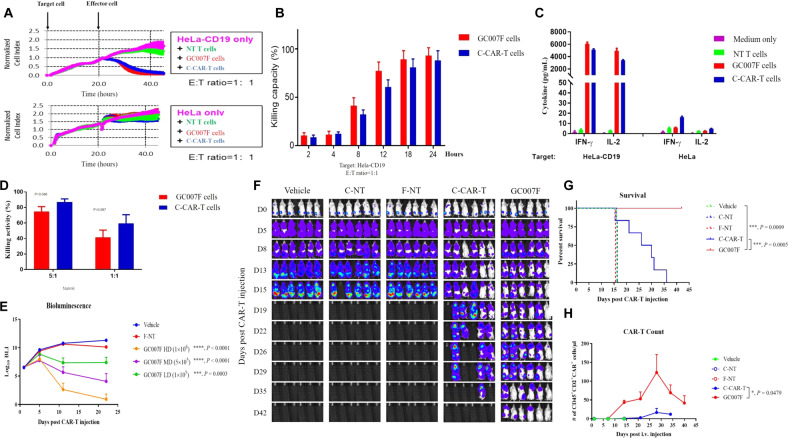
Fig. 3. In vivo and in vitro tumoricidal effects of GC007F cells.
A The specific killing of HeLa-CD19 cells was detected by RTCA assays. B Growth curves for HeLa-CD19 cells in the GC007F cell- and C-CAR-T cell-treated groups. C The concentrations of IFN-γ and IL-2 in the culture supernatant were quantified using ELISA. D CD19+ Nalm6-luciferase cells were cocultured with CAR-T cells at different ratios, and the cell-killing efficacy (%) was determined by measuring luciferase activity. E The tumor burdens in mice treated with different doses of GC007F cells were measured using IVIS. HD: high dose, MD: medium dose, LD: low dose. F Bioluminescence imaging of the tumor burden at the indicated time points after CAR-T cell infusion (5 × 105 cells). G Survival of tumor-bearing mice treated with GC007F cells, C-CAR-T cells, or the corresponding nontransduced (NT) controls (C-NT or F-NT cells). H The expansion of infused CD45+CD2+CAR+ T cells in the peripheral blood was quantitated using flow cytometry. Data are representative of two or more independent experiments. All data represent the mean ± SEM (n ≥ 6 per group) and were analyzed using two-way ANOVA (E, versus vehicle), the Mantel-Cox test (G), or a paired t test (H).