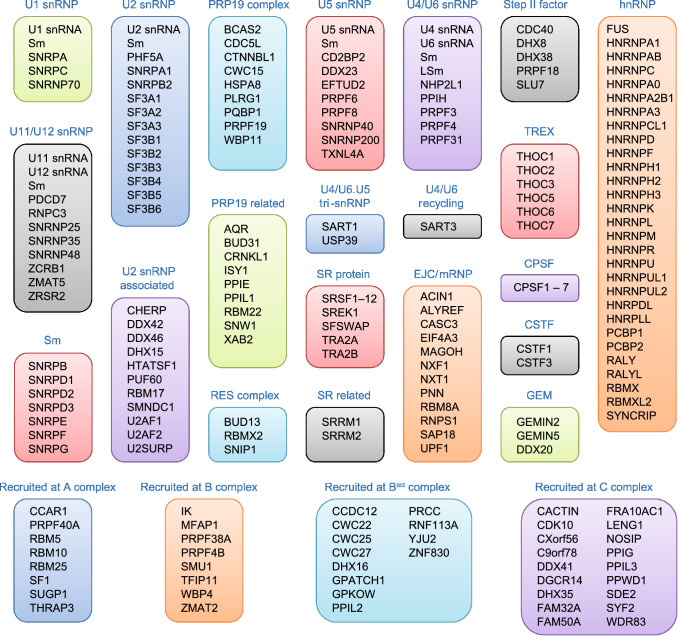
Figure 1.
The human spliceosome machinery. Human spliceosome consists of several snRNPs. Each snRNP is composed of a uridine-rich small nuclear RNA (U snRNA), Sm proteins (i.e., SNRPB/B′, D1, D2, D3, E, F, and G) or LSm proteins (i.e., LSm2–8), and a variable number of particle-specific proteins. The U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP contains two sets of Sm proteins and one set of LSm proteins. Classification is based on molecular features (e.g., SR proteins), association with stable spliceosome sub-complexes like the snRNPs or PRP19 complex, and other common designations (e.g., hnRNP, step II factors). Proteins that do not associate specifically with a given complex, such as general RNA binding factors, are not included in this figure. All protein names listed are official symbol from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database. The figure was illustrated based on the complex analysis results that were collected in the Spliceosome Database (Cvitkovic and Jurica 2013). Abbreviations: RES, retention and splicing; SR, serine and arginine-rich; EJC, exon junction complex; mRNP, messenger ribonucleoprotein; TREX, transcription-export; CPSF, cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor; CSTF, cleavage stimulation factor; GEM, gemini of coiled bodies; hnRNP, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein