Extended Data Fig. 2. Curbing bystander editing of the RAB7A transcript.
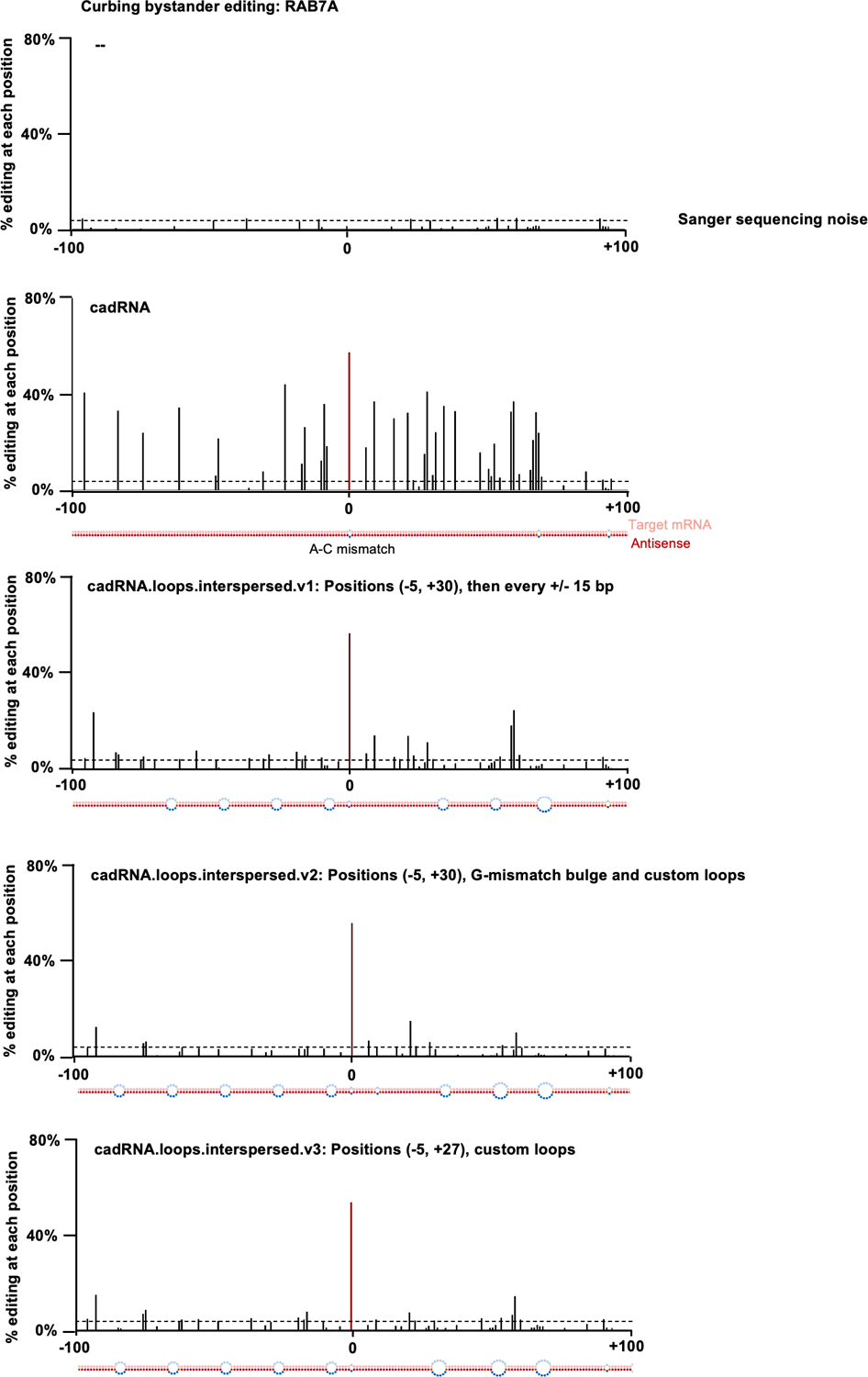
Histograms of percent A-to-G editing within a 200 bp window around the target adenosine in the RAB7A transcript as quantified by Sanger sequencing. The target adenosine is located at position 0. The dsRNA stretch formed between the antisense and the target are shown below each histogram. Design 1 (cadRNA): Unmodified circular.200.100 antisense, in addition to the A-C mismatch at position 0, two mismatches are seen at positions +66 and +91 that were created to avoid a stretch of poly Us to allow for transcription from a U6 promoter. Design 2 (cadRNA.loops.interspersed.v1): Loops of size 8 bp created at position −5 and +30 relative to the target adenosine and additional 8 bp loops added at 15 bp intervals along the antisense strand. Design 3 (cadRNA.loops.interspersed.v2): As compared to v1, a G-mismatch was positioned opposite a highly edited A (at position +9), an additional 8 bp loop was added at position −81 and the loop at position +49 was changed to a 12 bp loop. Design 4 (cadRNA.loops.interspersed.v3): As compared to v1, the 8 bp loop at +30 was changed to a 12 bp loop starting at position +27, one additional 8 bp loop was added at position −81 and the loop at position +49 was changed to a 12 bp loop. Values represent mean % editing (n=2). All experiments were carried out in HEK293FT cells.
