Figure 5. Loss of BMAL1 function in NAc astrocytes increases operant food self-administration and motivation during the day.
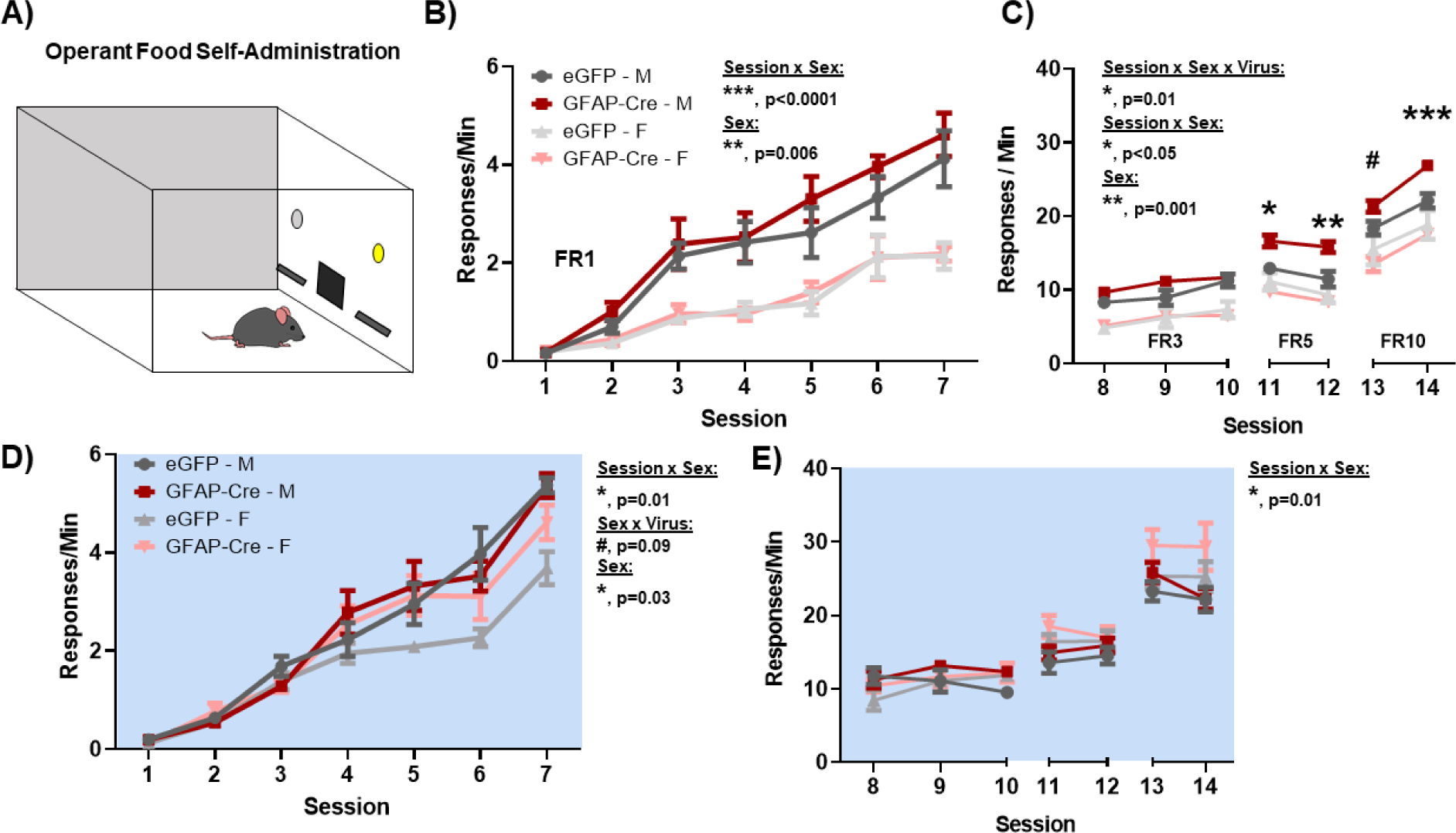
To assess natural reward and reward-motivation, both BMFL mice expressing NAc-specific GFAP-Cre or eGFP control were trained to self-administer food pellets in an operant food self-administration task both during the day and at night. (A) Mice were trained to discriminate between an active and an inactive lever, whereby active lever pressing resulted in a fixed ratio (FR) of food pellets. (B) On an FR1 schedule (i.e., 1 lever press : 1 pellet), GFAP-Cre mice successfully learn to self-administer food (Main effect of Session: F(6, 60) = 59.63, p<0.0001), but show no significant differences relative to controls (Virus: F(1, 10) = 1.68, p=0.22). In both virus groups, males show a significantly greater response rate relative to females (Sex: F(0.4, 4) = 37.11, ** p=0.006; Session × Sex: F(3.5, 35.2) = 8.52, *** p<0.0001). (C) To test reward motivation, mice were tested across increasingly difficult FR schedules (i.e., FR3, 3 presses : 1 pellet; FR5, 5 presses : 1 pellet; FR10, 10 presses : 1 pellet). GFAP-Cre male mice not only show a robust maintenance, but also a significant increase in food self-administration rate across FR schedules during the day, relative to control counterparts (Session × Sex × Virus: F(6, 59) = 2.96, * p=0.01; Sex × Virus: F(1, 10) = 5.09, * p<0.05; Sex: (F(0.6, 6) = 34.92, ** p=0.001). No effect of the virus was seen in female mice. (D) During the night, GFAP-Cre mice also successfully learn to self-administer food (Main effect of Session: F(7, 70) = 164.4, p<0.0001), with a main effect of sex (Sex: F(0.37, 3.7) = 15.01, * p=0.03; Session × Sex: F(2.8, 25.96) = 3.55, * p=0.03; Sex × Virus: F(1, 10) = 5.05, * p=0.04), but no significant effects of virus (Virus: F(1, 10) = 2.29, p=0.16). (E) During the night, no significant differences are seen in motivation as mice are tested across increasing FR schedules (Session × Sex × Virus: F(6, 58) = 1.1, p=0.37; Sex × Virus: F(1, 10) = 0.09, p=0.76 ; Sex: F(0.37, 3.67) = 2.17, p=0.17; Session × Sex: F(2.5, 24.32) = 4.75, * p=0.01). White background indicates behavior run during the day (ZT 2–6). Blue background indicates behavior run during the night (ZT 14–18). Mean ± SEM; n = 6; # p=0.07, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p=0.0001.
