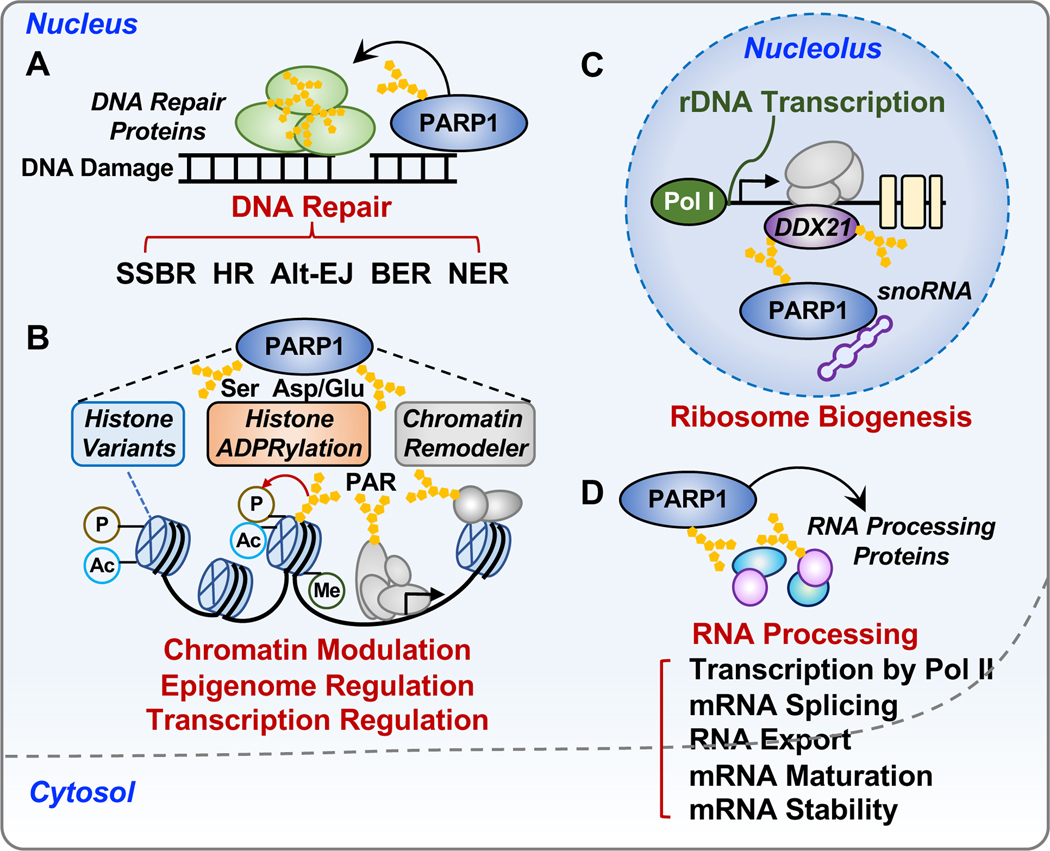
Figure 4. Biological functions of PARP1 in the nucleus.
PARP1 regulates a broad array of processes in the nucleus, such as DNA repair, chromatin regulation, gene expression, ribosome biogenesis, and RNA processing.
(A) Roles of PARP1 in DNA damage repair networks, including single-strand break (SSB) repair, base excision repair (BER), nucleotide excision repair (NER), and DSB repair through both homologous recombination (HR) and alternative end-joining (Alt-EJ) pathways.
(B) Roles of PARP1 in chromatin regulation. PARP1 modulates the structure and function of chromatin through the (1) regulation of chromatin composition, including histone variants and linker histone; (2) regulation of histone ADPRylation and other histone PTMs, including phosphorylation, acetylation and methylation; and (3) regulation of chromatin remodelers.
(C) Roles of PARP1 in ribosome biogenesis. SnoRNA-mediated activation of PARP1 promotes PARylation of DDX21, a DEAD-box RNA helicase in the nucleolus, resulting in the enhanced rDNA transcription and subsequent protein synthesis.
(D) Roles of PARP1 in RNA biology. PARP1 regulates multiple steps of RNA processing by interacting with and modifying RNA binding proteins and RNA processing factors.