Figure 1 |. Conditional inactivation of mitochondrial complex III subunit QPC in SIX2 nephron progenitor cells results in severe kidney dysplasia.
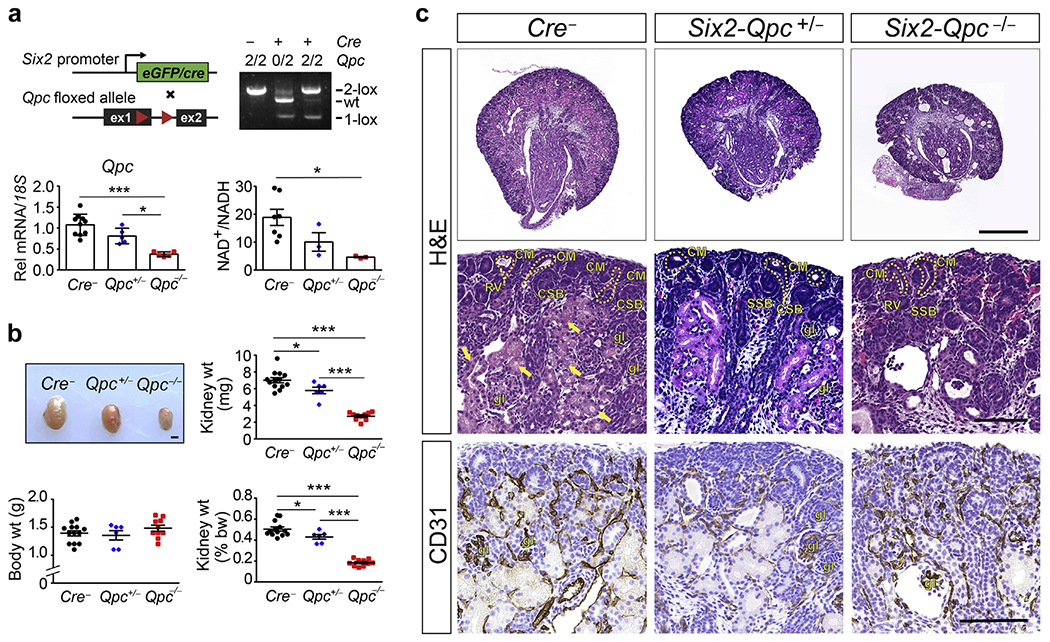
(a) Upper panels: schematic illustrating the experimental approach and location of targeted sequences within the conditional Qpc allele; loxP sites are depicted by red arrows. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of total genomic DNA isolated from Cre− littermate controls, Six2-Qpc+/− and Six2-Qpc−/− kidneys at postnatal day (P) 0. The genotype of mice is indicated; the number 2 represents the 2-lox non-recombined allele, and the plus and minus signs indicate the presence or absence of the Cre transgene. Lower-left panel: Qpc transcript levels in control, Six2-Qpc+/− and Six2-Qpc−/− kidneys at age P0 analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (n = 5–6). Lower-right panel: NAD+/NADH ratio in whole kidney tissues (n = 3–5). (b) Macroscopic images of kidneys from Cre− littermate control, Six2-Qpc+/− and Six2-Qpc−/− mutants at age P0. Bar = 1 mm. Kidney weight (wt), body weight, and kidney/body weight ratio at P0 (n = 8). (c) Representative images of kidney sections from control, Six2-Qpc+/− and Six2-Qpc−/− mice at age P0 stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for cluster of differentiation 31 antigen (CD31). Ureteric buds are outlined by dashed lines. Bar = 500 μm for the top panel and 100 μm for H&E stains and IHC sections. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; Student’s t test, 2-tailed, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. 18S, 18S ribosomal RNA; CM, cap mesenchyme; CSB, comma-shaped body; gl, glomerulus; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; Rel, relative; RV, renal vesicle; SSB, S-shaped body. To optimize viewing of this image, please see the online version of this article at www.kidney-international.org.
