Figure 2.
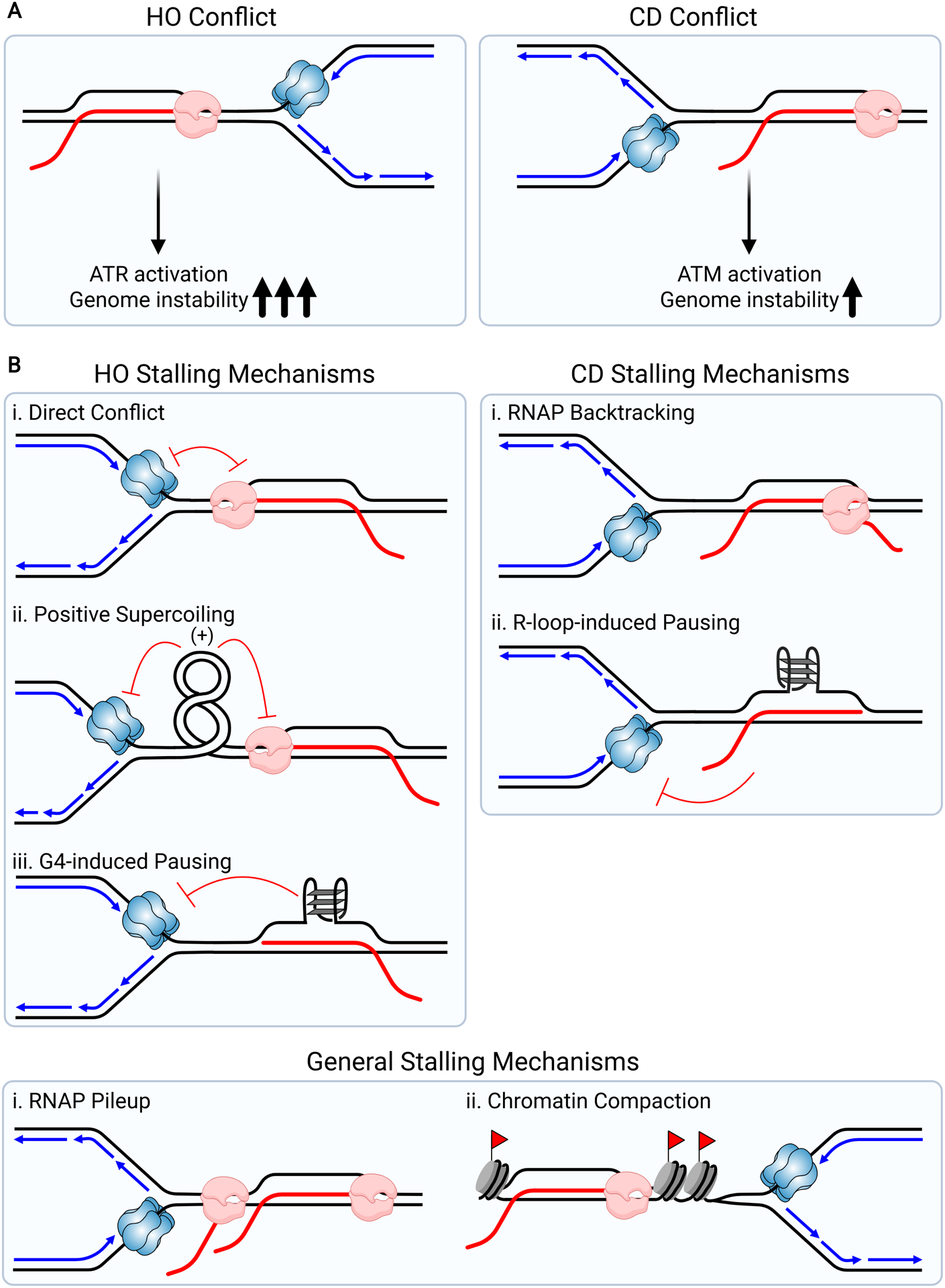
Factors Contributing to Replication Fork Stalling at R-loops. (A) Illustrates the two orientations in which a replication fork can encounter a R-loop, leading to a TRC. Head-on conflicts (HO, left) activate ATR and codirectional conflicts (CD, right) activate ATM. HO conflicts with R-loops are associated with greater genome instability. (B) Illustrates potential mechanisms that cause fork slowing in the HO (left) and CD (right) orientation. Flags represent epigenetic markers that promote chromatin compaction.
