Figure 7.
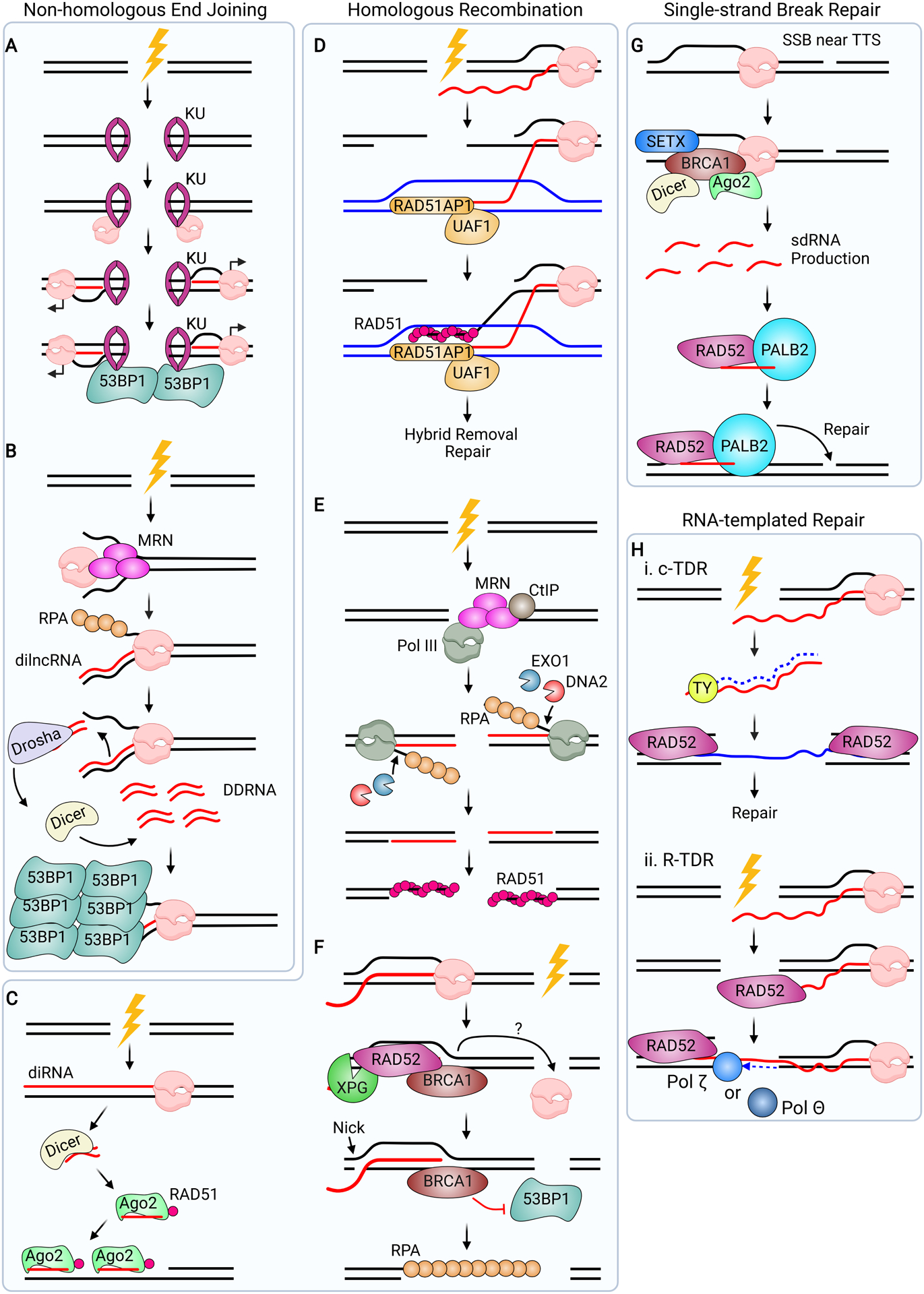
Roles for R-loops and Hybrids in DNA Repair Pathways. (A) During NHEJ, KU recognizes the DSB break ends and recruits RNAPII. RNAPII may transcribe de novo RNA from the break site and recruit 53BP1. (B) MRN binds to DNA ends and melts the duplexed DNA. MRN also recruits RNAPII, which initiates de novo RNA synthesis, forming dilncRNAs. These RNAs are consecutively processed by Drosha and Dicer, generating DDRNAs (red dsRNAs). DDRNAs promote 53BP1 recruitment and aggregation, and NHEJ repair. (C) During HR, RNAPII synthesizes diRNA at the break site. diRNAs are processed by Dicer, and Ago2 interacts with the product. Ago2 binds RAD51 and localizes it to the break site, likely forming a hybrid between the processed diRNA and the resected end. (D) When a DSB occurs in an actively transcribed region, a complex of RAD51AP1 and UAF1 facilitates ssRNA strand invasion into the donor DNA (blue). This stimulates RAD51-mediated ssDNA invasion into the donor template. The resulting structure is called a DR-loop. After hybrid removal, HR proceeds as normal. (E) MRN/CtIP recognize DSB ends and recruit RNAPIII, which initiates de novo RNA synthesis. The DNA flap is excised by EXO1 and DNA2. RNAPIII-mediated hybrid formation promotes RAD51 loading. (F) An R-loop forms at a break site when a DSB occurs in an actively transcribed locus. RAD52 recognizes the R-loop and recruits XPG and BRCA1 to the break site. BRCA1 inhibits 53BP1 at the break, while XPG cleaves the junction 5’ to the hybrid, initiating resection and RPA loading. (G) When a SSB occurs near an R-loop that forms at a transcription termination site, BRCA1 recruits SETX, Dicer, and Ago2 to the SSB, which generates sdRNAs. These RNAs are recognized by the RAD52/PALB2 complex, which localize to the SSB site and promote repair. (H) Should a DSB occur in a transcribed region, RNA can mediate repair via at least two distinct mechanisms. (i) The reverse transcriptase TY generates cDNA from the RNA transcript. RAD52 then promotes invasion of the cDNA into the break ends, and downstream processing occurs to complete repair. This pathway is called cDNA-templated repair (c-TDR). (ii) During RNA-templated repair (R-TDR), RAD52 promotes nascent RNA invasion into the upstream break end, creating an RNA bridge. The DNA Polymerases Polθ or Polζ can synthesize DNA from the template, repairing the break.
