Extended Data Fig. 8: Fc-mediated functions are dispensable for antibody-mediated protection against Lm.
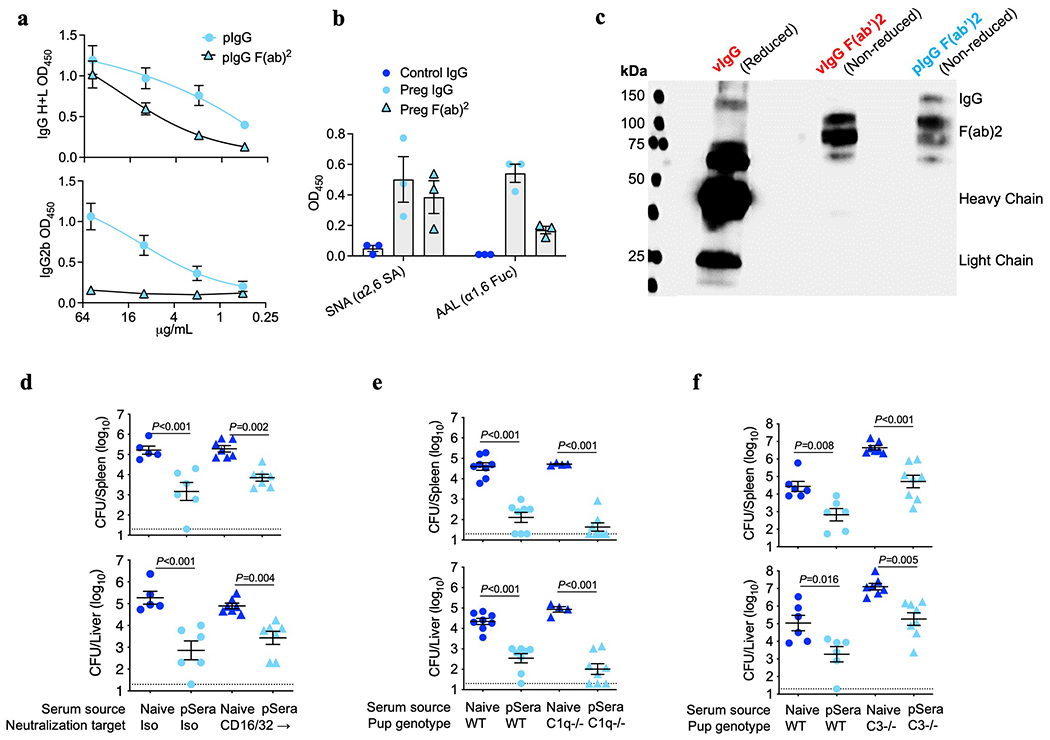
(a) Presence of IgG heavy (H) and light (L) chains or IgG2b Fc for pF(ab’)2 confirming efficient Fc removal after pepsin digestion. (b) Lectin staining for pF(ab’)2 compared with full-length pIgG for anti-LLO antibodies showing Fab glycosylation. SNA binds α2,6-linked sialic acid residues, while AAL binds α1,6-linked fucose. (c) SNA lectin blot comparing full-length IgG under reducing conditions to separate heavy and light chains, with purified F(ab’)2 fragments under non-reducing conditions, demonstrating preserved SNA lectin staining. (d) Bacterial burden after virulent Lm infection in neonatal mice transferred sera from preconceptual ΔActA Lm-primed pregnant/postpartum (pSera) or naive control mice, along with anti-CD16/32 blocking or isotype control antibodies. (e, f) Bacterial burden after virulent Lm infection in neonatal WT, complement C1q-deficient mice (e) or complement C3-deficient (f) transferred pSera or sera from naive mice. Pups were infected with virulent Lm 3-4 days after birth, 24 hours after antibody transfer, with enumeration of bacterial burden 72 hours post-infection. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, with graphs showing data combined from at least 2 independent experiments each with 3-5 mice per group per experiment. Gel is representative of results from 3 independent experiments each with similar results (c). Bar, mean ± standard error. P values between key groups are shown as determined by one-way ANOVA adjusting for multiple comparisons. Dotted lines, limit of detection.
