Extended Data Fig. 1: Pregnancy enables antibody mediated protection against Lm infection.
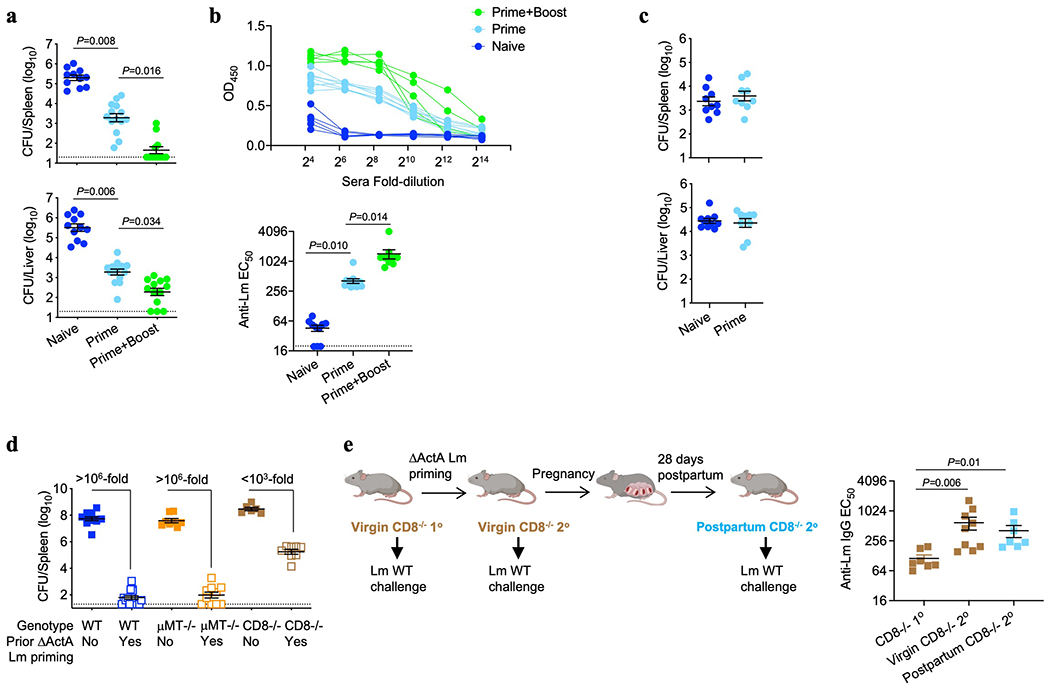
(a, b) Bacterial burden (a) and anti-Lm IgG titer (b) in neonatal mice infected with virulent Lm born to WT naive mice or mice preconceptual primed with ΔActA Lm once or twice 2 weeks apart. (c) C. albicans fungal burden in neonatal mice born to WT female mice primed with attenuated ΔActA Lm one week prior to mating or naive control mice. Pups were infected with virulent C. albicans 3 days after birth, with enumeration of pathogen burden 48 hours post-infection. (d) Bacterial burden 72 hours post-infection with virulent Lm in adult WT, μMT−/− or CD8−/− mice with or without ΔActA Lm priming 4 weeks prior. (e) Anti-Lm IgG titer in adult CD8−/− mice 3 days after primary Lm infection compared with secondary challenge of ΔActA Lm-primed virgin female mice or preconceptually ΔActA Lm-primed CD8−/− female mice 3 weeks post-partum. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, with graphs showing data combined from at least 2 independent experiments each with 3-5 mice per group per experiment. Bar, mean ± standard error. P values between key groups are shown as determined by one-way ANOVA adjusting for multiple comparisons. Dotted lines, limit of detection.
