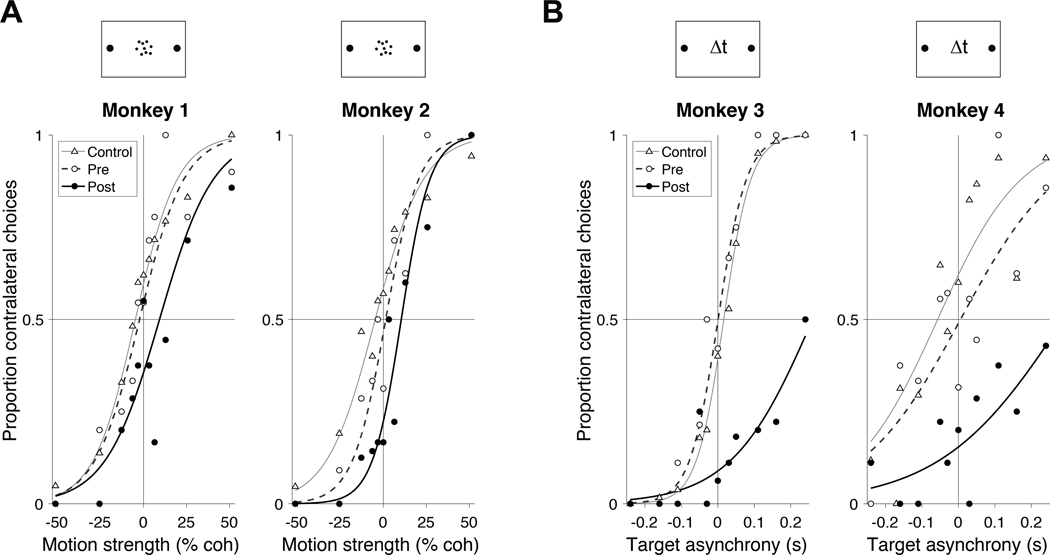
Figure 3: Inactivation of LIP induces a decision bias.
A, Proportion of contralateral choices as a function of motion strength for Monkeys 1 and 2. Filled circles show data from the first 100 trials after muscimol injection in the first inactivation session. Open symbols show data from the last 100 trials in the pre-injection phase of the same experiments. Triangles depict data from all control sessions using the first 100 trials after the saline or sham injection. Muscimol induces a bias against contralateral choices. Curves are logistic regression fits (Equation 2). B, Proportion of contralateral choices as a function of target onset asynchrony for Monkeys 3 and 4. Data from Monkey 3 are from the first session in which muscimol was administered. Data from Monkey 4 are from the session in which 0.3 mg/kg clozapine was administered. Other conventions are the same as in A. See Tables S1 and S2 for statistical analysis.