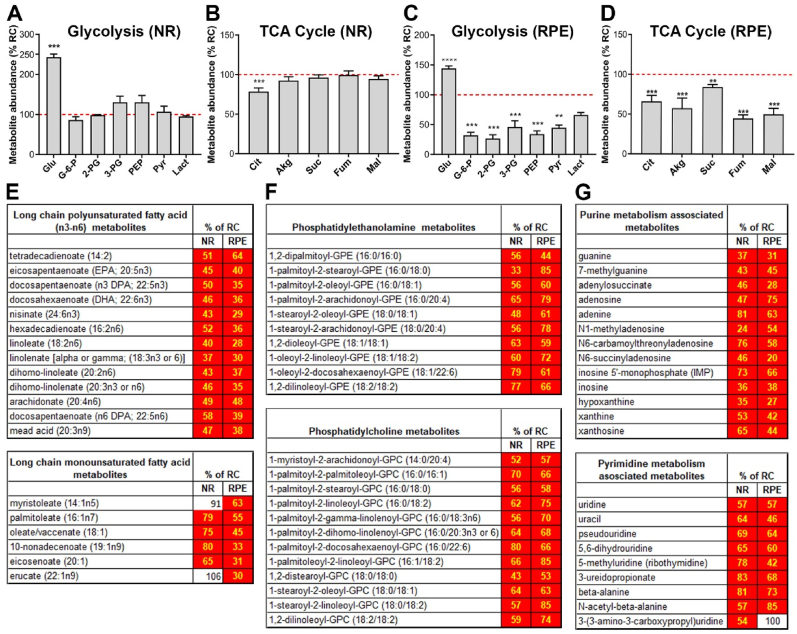
Fig. 4.
Retinal metabolic dysregulation precedes onset of the functional decline in mice on RDC diet. Steady-state levels of metabolites in mice fed on riboflavin-deficient chow (RDC) until P120 are presented as percent change from levels for age-matched littermate controls on regular chow (RC) for both NR and RPE-Ch. Glycolytic (A, C) and TCA cycle (B, D). Dotted red line represent levels in retinas of RC fed animals. Each respective class of metabolites is identified as a header in each table (E–G). Values which were not significantly different are in white boxes and those significantly lower are marked in red. Statistical analysis was assessed by t-tests with FDR correction for multiple tests (*p < 0.05 ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001, **** = p < 0.0001), with n = 6 samples for each dietary group. Each sample contained at least 6 independent retinas or RPE. Plotted are means ± SEM. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)