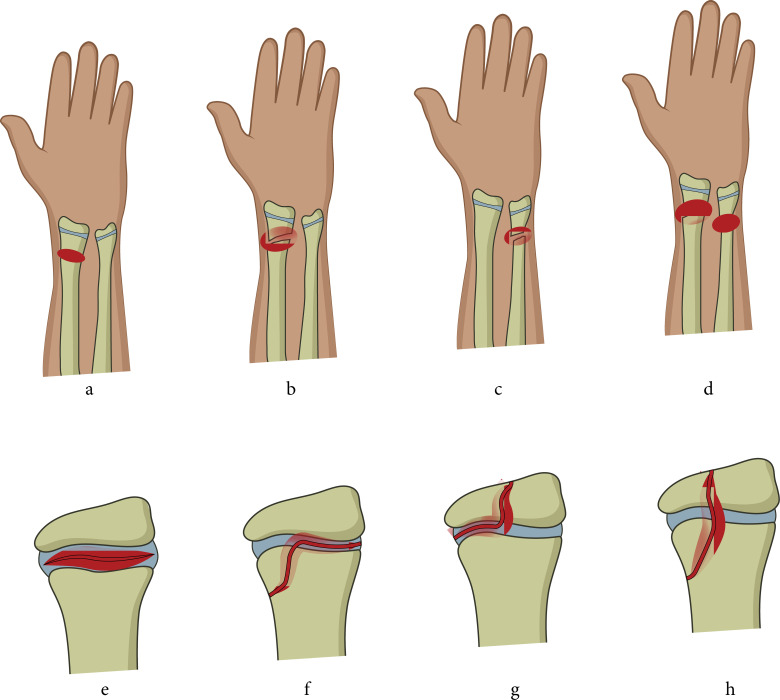
Fig. 1.
Included children with a distal forearm fracture. legends: a) greenstick fracture (no distinguishing between greenstick and torus fractures); b) complete radius fracture; c) complete ulna fracture; d) complete radius and ulna fracture (antebrachium fracture); e) SH type 1; f) SH type 2; g) SH type 3; and h) SH type 4.