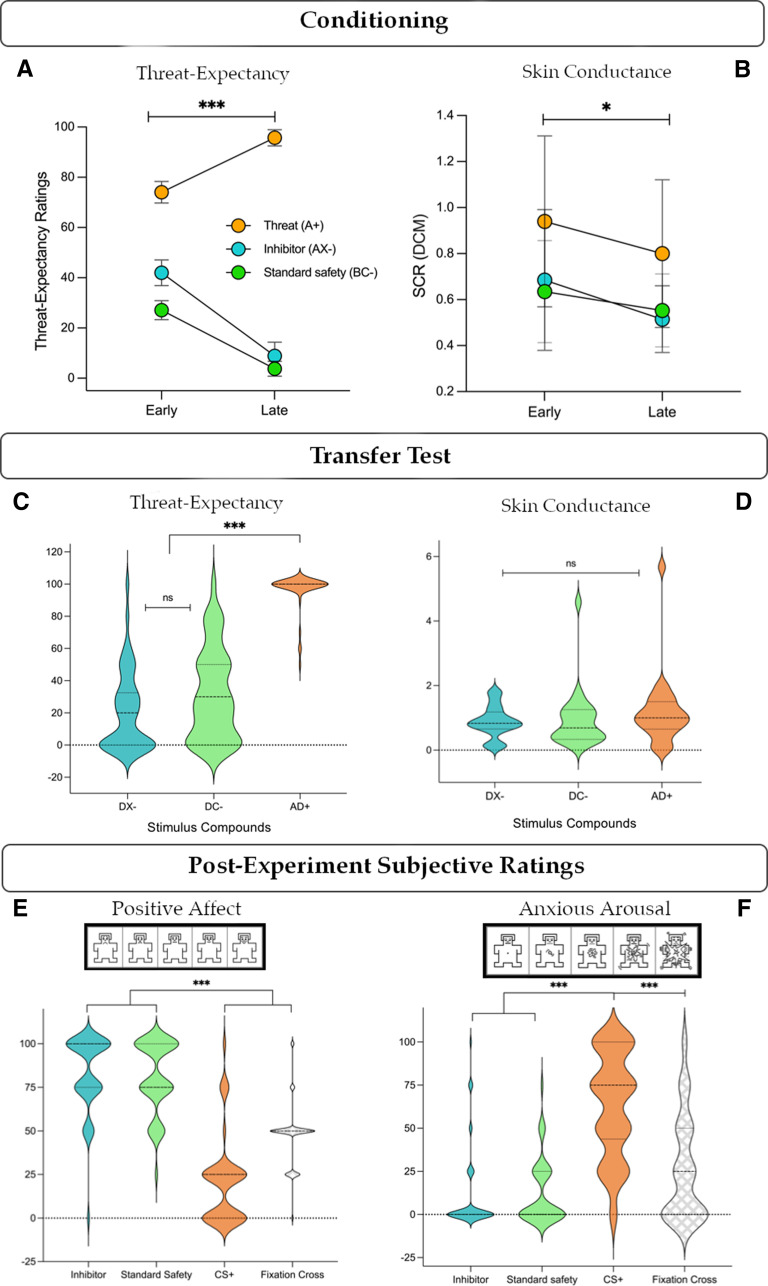
Figure 2.
Behavioral responses. A, Threat expectancy ratings showed a significant decrease across conditioning for each safety signal, with higher ratings during early trials for the inhibitor versus standard, and no difference during late conditioning. B, SCRs showed no difference between stimuli (inhibitor vs standard), but a significant decrease from early to late conditioning for each stimulus. C, Both safety signals inhibited threat expectancy at test compared with the threat compound AD+ but did not differ from one another. D, SCRs showed no differences at test. E, Subjective affective ratings reliably discriminated safety signals with high positive affect from the CS+ and neutral fixation cross. F, Similarly, safety signals elicited low appraisal of anxious arousal relative to high ratings of CS+, and moderate ratings of the fixation cross. AX–, conditioned inhibitor; BC–, standard safety signal; DX–, inhibitor + threat cue; DC–, standard safety signal + threat cue; AD+, threat compound; DCM, dynamic causal model for SCR (via PsPM). Error bars indicate 95% CIs. *p < 0.05. ***p < 0.001. ns, p > 0.05.