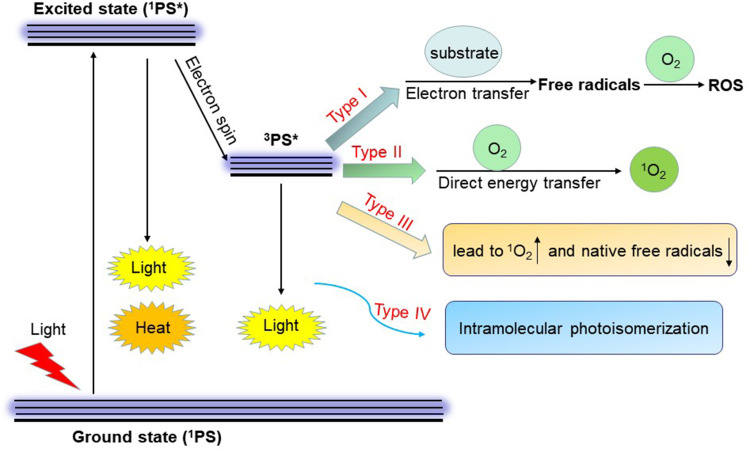
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of action of photodynamic therapy. Following light absorption, excited state 3PS* reacts with O2 to produce ROS and 1O2 (type I and II reactions). Type III PSs combine properties leading to the generation of 1O2 and reduction of native free radicals in target cells. Type IV mechanism involves a structural change from excited state 1PS* by photoisomerization to enable molecular target binding of the activated PS* to its cellular target site. (* represents the excited state).
Abbreviations: PS, photosensitizer; 1PS, singlet photosensitizer; 3PS, triplet photosensitizer; ROS, reactive oxygen species; 1O2, singlet oxygen; O2, oxygen.