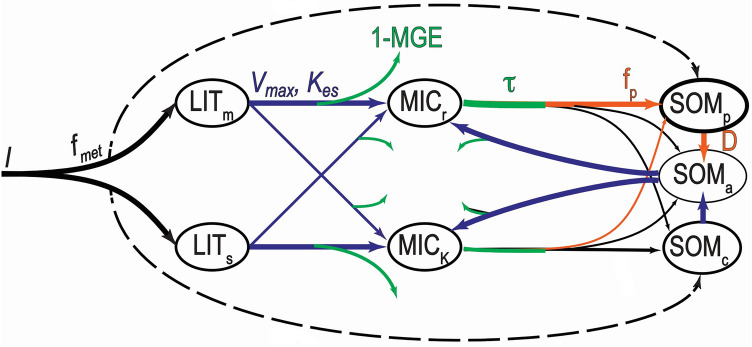
Figure 1.
Diagram of the MIcrobial-MIneral Carbon Stabilization (MIMICS) model, which explicitly considers microbial functional diversity by simulating two functional groups (MICr, inefficient, fast-growers; MICK, conservative, slow-growers) and their potential effects on litter decomposition and soil organic matter persistence (available SOMa; chemically protected SOMc; physically protected SOMp). Litter C inputs are initially partitioned (fmet) between litter pools (structural LITs; metabolic LITm), while a lesser fraction (fi) transfers directly to the SOM pools. Parameters used for model calibration and validation related to microbial catabolic capacity (Vmax and Kes, blue lines), microbial anabolism (MGE and τ, green lines), and physicochemical protection of SOM (fp and D, orange lines). See also Table 1.