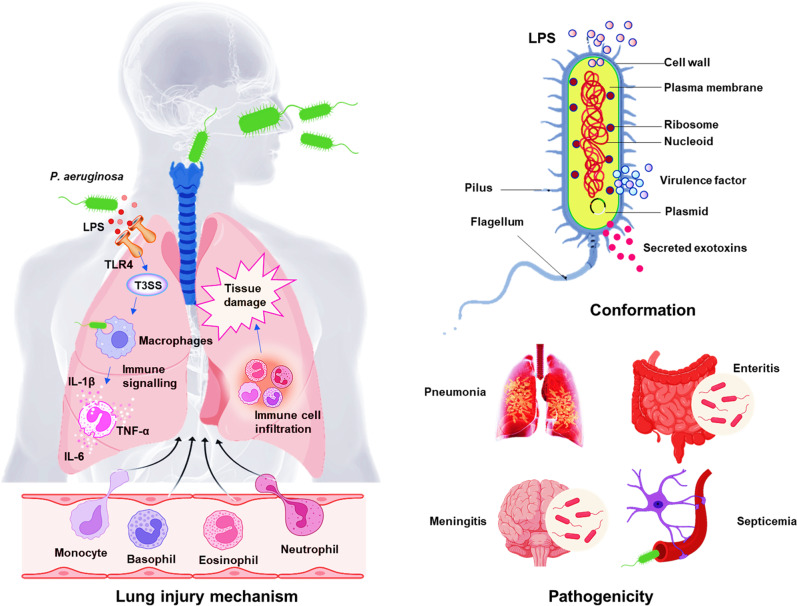
Fig. 1.
Schema of P. aeruginosa pathogenesis. P. aeruginosa can be traced everywhere including hospital environments and cause serious infection of almost any organ. LPS induces TLR-4-dependent and -independent inflammatory responses in the lung after bacterial infection, epithelial cells secrete cytokines and chemokines, thereby recruiting and activating innate immune cells and adaptive immune cells. The recruitment of neutrophils is a sign of inflammatory response activation. Although the activation of neutrophils is critical for host defense, excessively activated immune cell infiltration will cause severe tissue damage and aggravate bacterial infections.478 Therefore, studying the balance between the virulence factors secreted by bacteria and corresponding host immunity is important for the treatment of infections