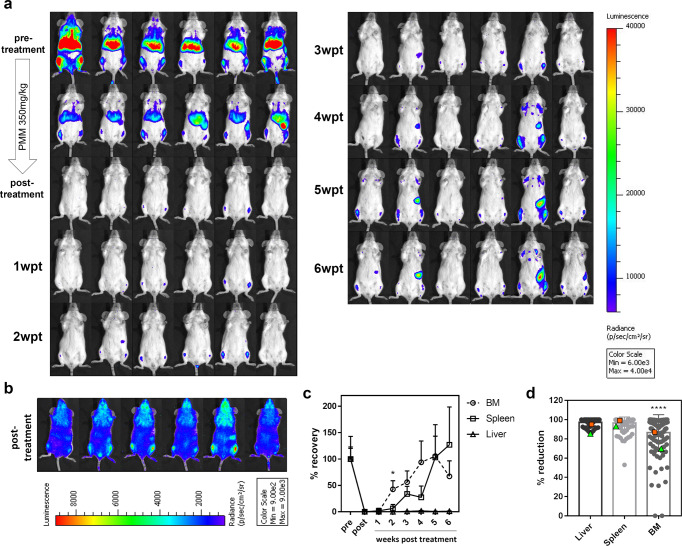
Fig. 1. Reproducible post-treatment relapse model using sub-curative paromomycin identifies the BM as niche for treatment failure.
a In vivo bioluminescent imaging (BLI) using an exposure time of 15 min of LEM3323 WTPpyRE9 infected BALB/c mice at 1-6 weeks post-treatment (wpt) at 350 mg/kg PMM s.i.d. IP for 5 days. b BLI (with sensitivity scale) at the end of treatment. c Mean relative luminescence units (RLU) values of BM and spleen during the first 6 weeks of LEM3323 WTPpyRE9 infection in BALB/c mice, where 100% is the pretreatment RLU and 0% the post-treatment RLU. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM, Mann-Whitney test (two-tailed), *p ≤ 0.05. a–c Groups consist of 3-6 BALB/c mice (three independent experiments). d Reduction in parasite burden after treatment of golden Syrian hamsters with a broad set (n = 90) of antileishmanial test compounds; treatments with >85% clearance in the liver were considered therapeutically relevant. As a reference, squares (orange) depict results with MIL, and triangles (green) represent SSG treatment. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (two-tailed), ****p ≤ 0.0001.