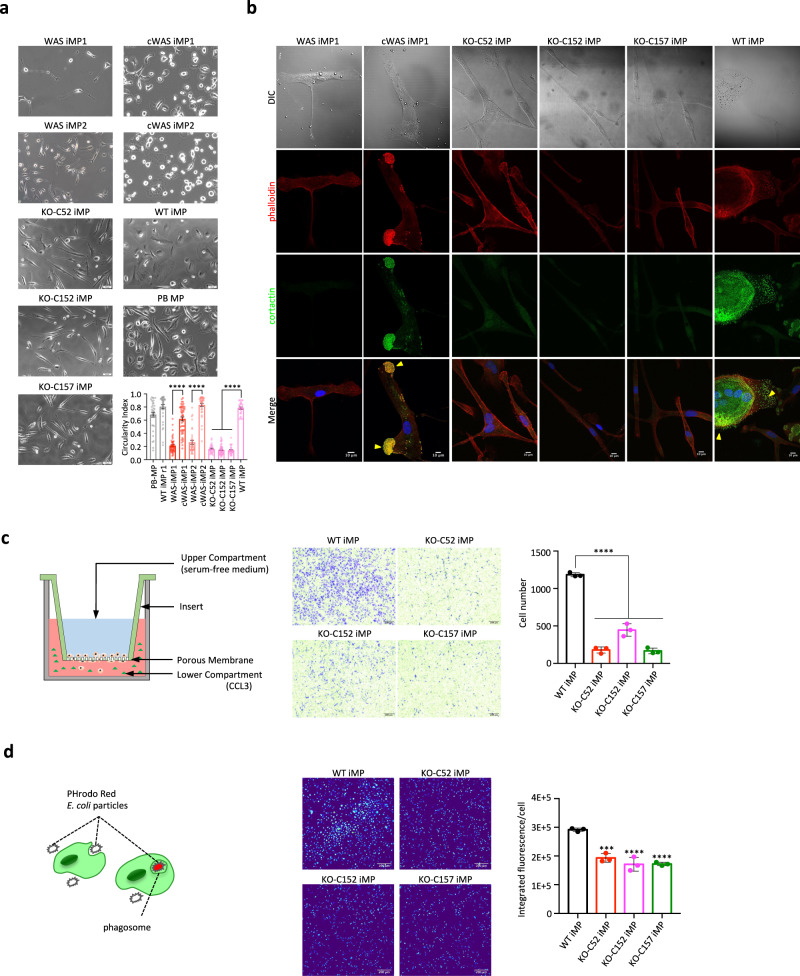
Fig. 2. Recapitulation of WAS phenotypes using isogenic WAS-iPSC models.
a Representative phase-contrast microscopy images of macrophages and quantitative analysis of their circularity. PB-MP: macrophages derived from normal peripheral blood. Analyzed cell n = 36 (PB-MP), 36 (WT iMP r1), 50 (WAS-iMP1), 50 (cWAS-iMP1), 36 (WAS-iMP2), 36 (cWAS-iMP2), 30 (KO-C52 iMP), 47 (KO-C152 iMP), 30 (KO-C157 iMP), and 28 (WT iMP). Data are shown as mean ± SEM, Two-sided Student’s t test, ****P < 0.0001. Scale bar = 50 μm. b Representative immunofluorescence images of podosomes (yellow arrowheads) in macrophages. Podosomes are marked by F-actin and cortactin (encoded by the CTTN gene). DNA was stained with DAPI. DIC differential interference contrast. Scale bar = 10 μm. The experiment was repeated three times independently. c Transwell migration assay. Left: schematic of the principle of the transwell migration assay. Each upper compartment was seeded with the same number of WT iMPs and KO-iMPs (three clones, three replicates). The images show macrophages that migrated to the underside of the porous membrane and were stained by crystal violet. Rightmost: quantitation of cell number in the images. Biological replicate n = 3. Individual dots represent cell number per sample, and the bars show mean ± SD, ****P = 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Scale bar = 200 μm. d Quantitative measurement of phagocytosis. Left: schematic of the principle of the phagocytosis assay using the pH-sensitive fluorescence dye pHrodo Red-conjugated E. coli particles. Right: fluorescence images and the quantification of pHrodo Red fluorescence in the same number of WT iMPs and KO-iMPs (three clones, three replicates). rightmost: quantitation of pHrodo Red fluorescence in each cell. Biological replicate n = 3, cell n = 2271 (WT iMP), 1653 (KO-C52 iMP), 1452 (KO-C152 iMP), 1180 (KO-C157 iMP). Data are shown as mean ± SD, ***P = 0.0001, ****P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Scale bar = 200 μm.