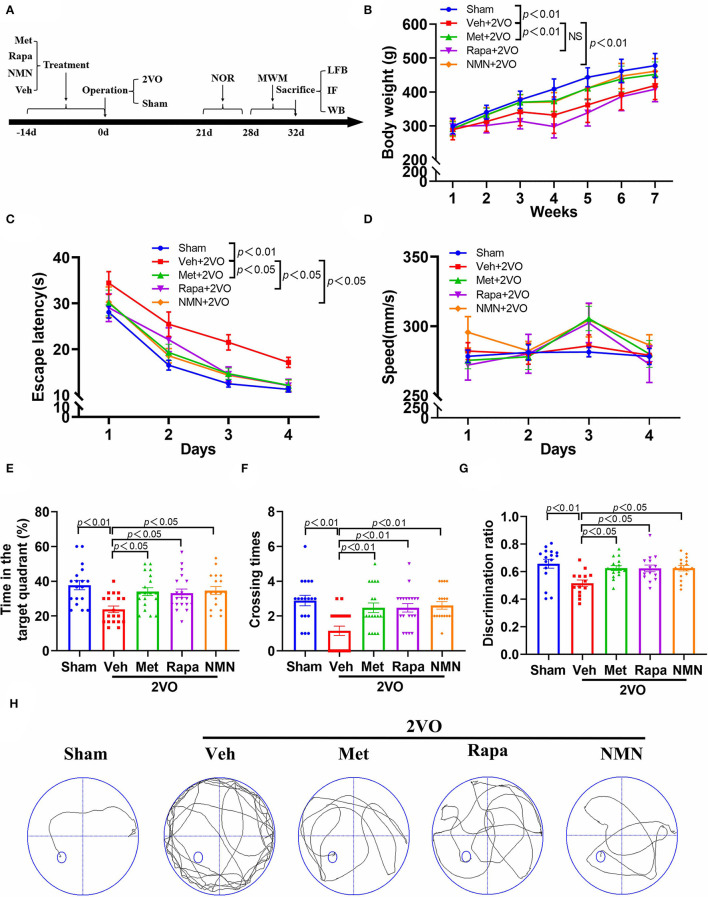
Figure 1.
Metformin, rapamycin, or NMN pretreatment improves cognitive impairment in BCCAO rats. (A) Experimental protocol. Rats received either saline (Veh), metformin (Met), rapamycin (Rapa), or NMN (NMN) at 2 weeks before surgery via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection daily for 14 consecutive days. The animals were scarified 32 days after surgery. (B) The body weight of rats from different groups (n = 20). The p-values were assessed by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. The escape latency (C) and swimming speed (D) during the training phase, and duration in the target quadrant (E), and the times crossing the area the platform placed in the training phase (F) during probe trial of MWM test (n = 18–19 per group). The p-values in C and D were assessed by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. The p-values in E and F were assessed by Kruskal–Wallis test with a Dunn post-test. (G) The discrimination ratio in novel object recognition test (n = 14–16 per group). The p-values were assessed by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey's test. (H) Representative trajectories in swim path in sham-operated rats and BCCAO rats treated with Veh, Met, Rap, or NMN. All data were shown as mean ± SEM. 2VO, two-vessel occlusion; NOR, novel objective recognition; MWM, Morris water maze; LFB, Luxol fast blue staining; IF, immunofluorescence; WB, Western blot; and NS, not significant.