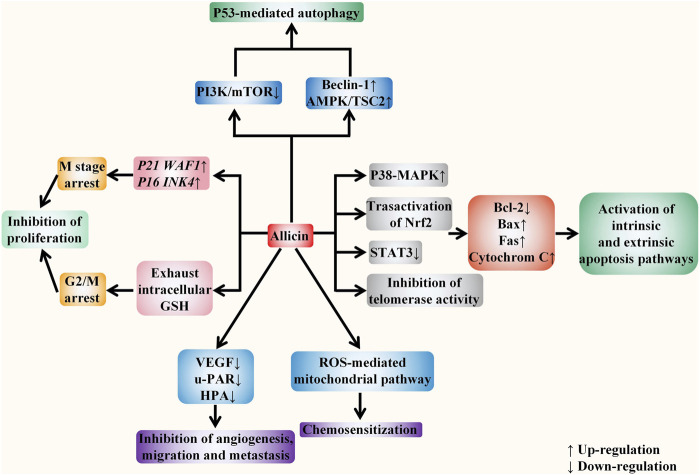
FIGURE 5.
Allicin acts against digestive system cancers in vitro. The anticancer effect of allicin in vitro is mainly reflected in five aspects, including inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, inducing autophagy, inhibiting angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis, and enhancing the sensitivity of tumor chemotherapy. It depletes intracellular glutathione (GSH) and up-regulates p21WAF1 and p16INK4 genes to block the cell cycle and inhibit cell proliferation. It activates both endogenous and exogenous apoptotic pathways by regulating intracellular signaling pathways, inhibiting telomerase activity, and regulating the activity of apoptosis-related proteins. In addition, it also down-regulates the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway and up-regulates the AMPK/TSC2 and Beclin-1 signaling pathways to induce the P53 mediated autophagy. It inhibits tumor angiogenesis, migration, and metastasis by down-regulating VEGF, u-PAR, and HPA. Moreover, via ROS -mediated mitochondrial pathway, it exerts the chemosensitization effect towards tumor cells.