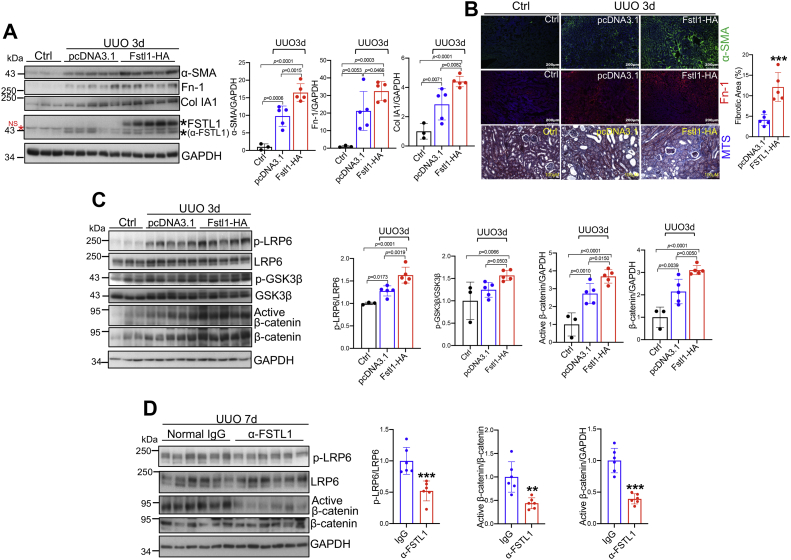
Figure 2.
Impacts of overexpression and neutralization of FSTL1 on renal fibrosis and on thecanonical Wnt/β-catenin pathways in UUO kidneys.A–C, effects of FSTL1 overexpression on renal fibrosis and on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Male mice at 8 weeks of age were subjected to UUO on left ureters. FSTL1-HA or pcDNA3.1 plasmid was injected via the tail vein on day 2 after UUO surgery. Mice were sacrificed the next day, and right (Ctrl) and left (UUO) kidneys were collected for analysis. A, kidney lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for FSTL1 expression and the fibrosis markers α-SMA, fibronectin-1 (Fn-1), and collagen 1 (Col IA1) (left panel). Levels of α-SMA, Fn-1, and Col IA1 relative to GAPDH are presented (right panels). B, immunofluorescence for α-SMA and Fn-1 and Masson’s trichrome staining (MTS) on sections from the UUO kidneys of mice injected with pcDNA3.1 or FSTL1-HA plasmids. Frozen sections were used for immunofluorescent staining for α-SMA (green) and Fn-1 (red). Paraffin sections were used for MTS. The fibrotic blue area was quantified. C, kidney lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (p-LRP6, p-GSK3β, active β-catenin, and β-catenin) (left panel). Levels of p-LRP6 relative to LRP6; p-GSK3β relative to GSK3β; and active β-catenin and β-catenin relative to GAPDH are presented (right panels). D, effects of neutralization of FSTL1 on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Male mice at 8 weeks of age were subjected to UUO on left ureters. Normal goat IgG or goat anti-FSTL1 antibody was injected (i.p.) at 5 μg/g body weight 7 days after UUO surgery. About 6 h later, kidney samples were harvested: kidney lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for p-LRP6, active β-catenin, and β-catenin (left panel). Levels of p-LRP6 relative to LRP6 and active β-catenin relative to β-catenin and GAPDH are presented (right panels). ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. FSTL1, follistatin-like 1; HA, hemagglutinin; IgG, immunoglobulin G; LRP6, low-density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 6; α-SMA, alpha-smooth muscle actin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; UUO, unilateral ureteral obstruction.