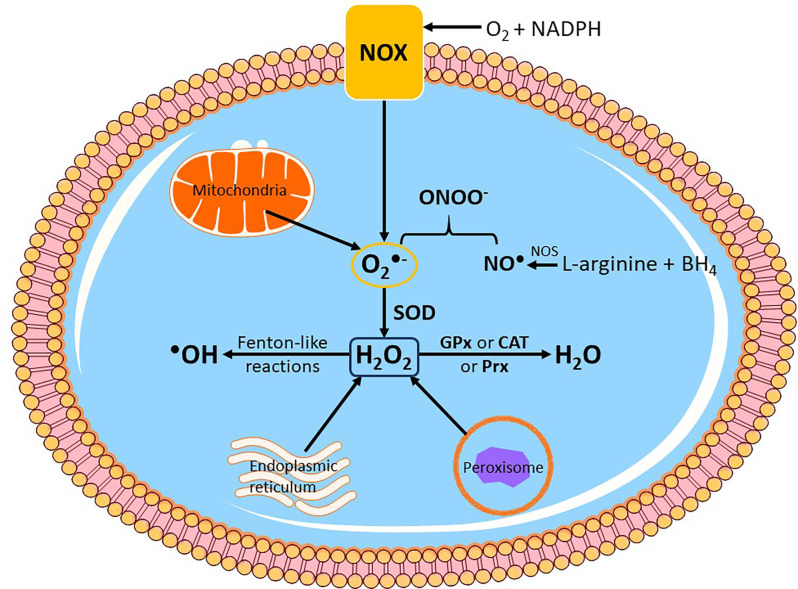
Figure 2.
Endogenoussources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Intracellular ROS is mainly produced by subcellular organelles such as the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and peroxisomes. Another enzymatic system that produces ROS and is located on the cytoplasmic membrane is NADPH oxidase (NOX), which primarily generates superoxide anion radical (O2●−). In mitochondria, O2●− is mainly produced by complexes I and III. Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) catalyzes the formation of nitric oxide (NO●) from L-arginine and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), and subsequently NO● can yield peroxynitrite (ONOO−) by direct reaction with O2●−. Cytosolic O2●− is then converted to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by endogenous superoxide dismutase (SOD). H2O2 can be further reduced to water (H2O) by the antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT) or peroxiredoxin (Prx), or react with metal cations in Fenton and Fenton-like reactions to generate hydroxyl radical (●OH), which can cause immediate oxidative damage to biomolecules.