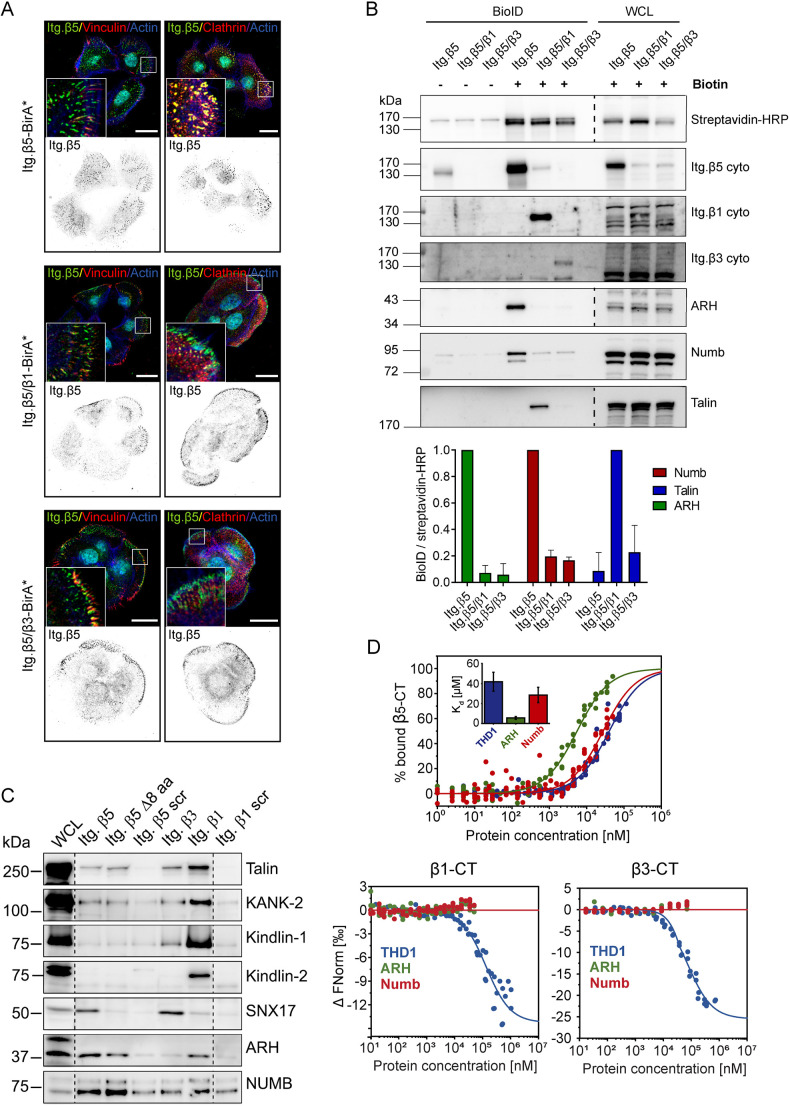
Fig. 2.
Adaptor protein binding to integrin β subunits. (A) Colocalization of integrin chimeras fused to the promiscuous biotin ligase BirA* (green in merge) with vinculin (red; left panels) or clathrin (red; right panels) in PA-JEB/β4 keratinocytes. Actin is shown in blue. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (cyan). Scale bars: 20 μm. (B) Representative western blots of BioID assays performed using the integrin chimeras shown in A. Quantifications of ARH, Numb and talin signal intensities normalized to streptavidin-HRP levels are shown (n=3; bars show mean±s.d.). (C) Representative western blots of pulldown assays (from two repeats) using synthetic integrin β cytoplasmic domains in RAC-11P cell lysates. (D) MST assay demonstrating binding of ARH, Numb, and talin-1 head domain (THD1) peptides to the β5 cytoplasmic domain (n≥5). Inset in top panel shows calculated Kd (mean±s.d.). β5-CT, β5 cytoplasmic tail; β5 Δ8 aa, β5 mutant carrying a deletion of a stretch of 8 amino acids (Val783–Phe790) located between the NPxY and NxxY motifs in the cytoplasmic domain of β5; Itg. β5/β1, chimeric receptor containing the extracellular and transmembrane domain of β5 and the cytoplasmic domain of β1; Itg. β5/β3, chimeric receptor containing the extracellular and transmembrane domain of β5 and the cytoplasmic domain of β3; scr, scrambled; WCL, whole-cell lysates.