Figure 2.
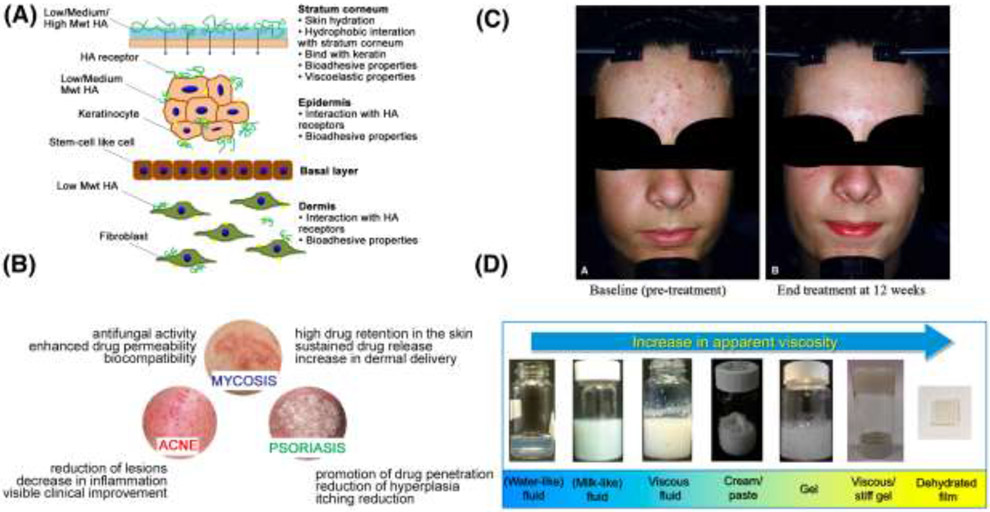
The set of design criteria for a manufacturer of topical hydrogel-based formulations are highlighted. Panel (A) is a schematic of the proposed mechanisms for the skin permeability of hyaluronic acid. [106] High MW HA primarily interacts with the stratum corneum through hydrophobic interactions, while some low MW HA can even permeate into dermis This greatly informs design choices for topical facial applications. (B) is a schematic illustration of the effects of hydrogels in the treatment of selected skin diseases that affect the head and face. [107] These treatments are commercially available as hydrogel formulations that can be topically applied. (C) is a depiction of a typical patient before and after treatment with a combination clindamycin/tretinoin hydrogel for acne vulgaris [96] (D) is a depiction of a range in the apparent viscosity and appearance of lipid-based systems and emulsion for cosmetic applications. Apparent viscosity increases from a water-like liposome solution to a dehydrated film of a stiff gel. [97]