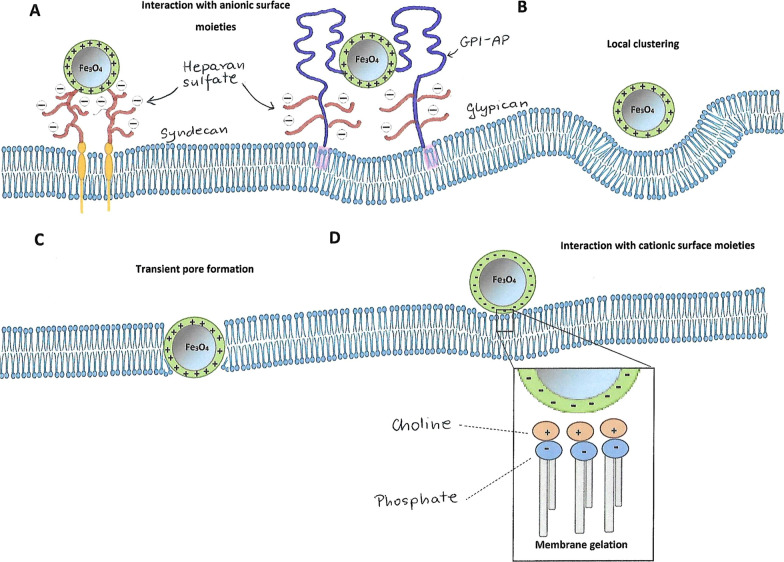
Fig. 7.
Interactions between positively (A–C) and negatively (D) charged magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) and the plasma membrane. Electrostatic interactions with cationic MNPs and anionic syndecans and glypicans containing heparan sulfate (A). Nonspecific cationic MNPs interactions with anionic phospholipids (B). Transient pore formation by small cationic MNPs (≤ 20 nm) due to the strong attraction to the inner membrane layer in phosphatidylserine-rich regions (C). Local membrane gelation induced by anionic MNPs in phosphatidylcholine-rich membrane microdomains (D)