Fig. 1.
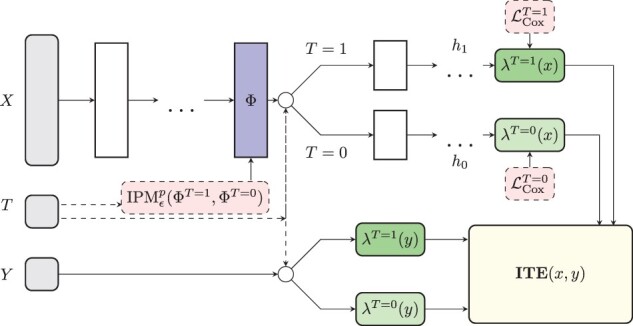
The BITES network architecture. BITES uses shared deeply connected layers for both treatment options, which are mapped on a latent representation . This is regularized by a Sinkhorn divergence to account for imbalances between treatment and control distributions. The factual and counterfactual proportional hazard rates are modeled by two different outcome heads (h1 and h0), respectively. These are used to predict the ITE together with the corresponding baseline hazard function. The latter is individually estimated for treatment and control patients
