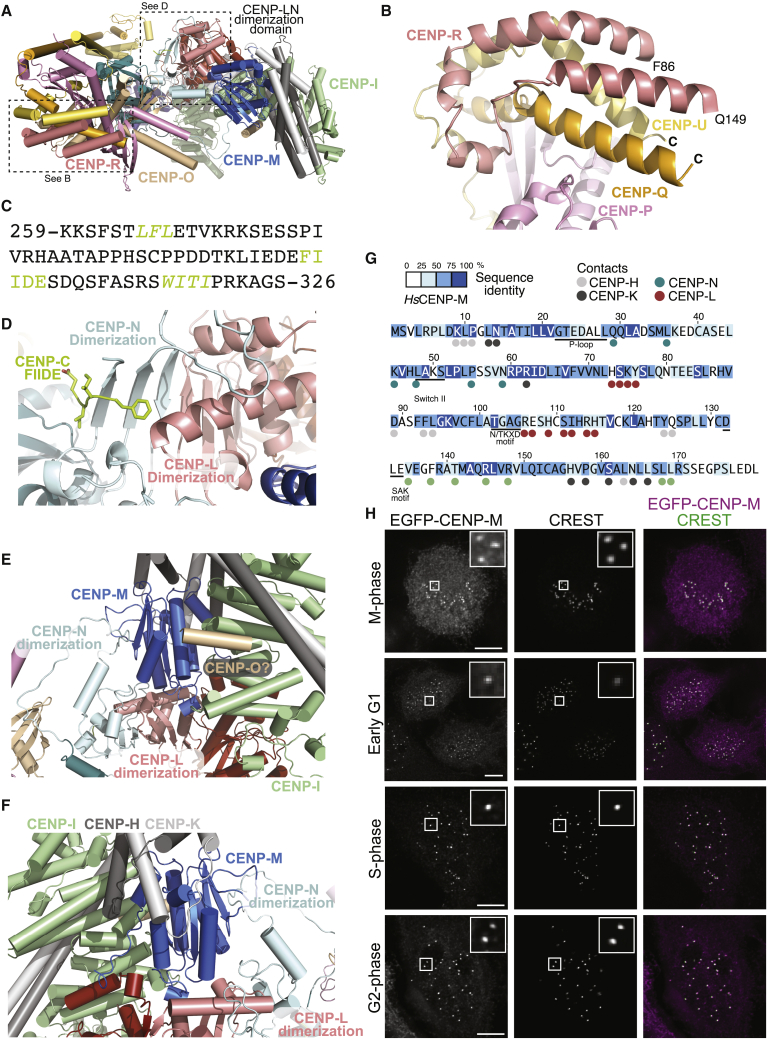
Figure 2.
CENP-C, CENP-M, and CENP-R
(A) Cartoon of human CCAN viewed from above (relative to Figure 1C), with the “knob” domain of pillar 1, the dimerization domain of the CENP-LN vault, and the upper domain of pillar 2 with CENP-M.
(B) Close-up view of the two helices of CENP-R, with visible residues and connecting helical segment.
(C) Sequence of HsCENP-C within the CCAN-binding region. Two sequences (green and italics) identify motifs shown to interact with CENP-LN and CENP-HIKM (Klare et al., 2015). The FIIDE motif interacts with the CENP-LN dimerization domain.
(D) Cartoon model of the CENP-LN dimerization domain with bound CENP-C FIIDE motif in sticks. See Figure S5F for corresponding density.
(E) Embedding of CENP-M in a network of interactions between pillar 2 and the vault.
(F) A rotated view showing additional CENP-M interactions.
(G) Sequence of CENP-M with conservation in 12 distant CENP-M orthologs and contacts with neighboring subunits (adapted from Basilico et al., 2014). CENP-M residues contacting other CCAN subunits are identified with the color of the interacting subunit.
(H) Localization of EGFP-CENP-M in HeLa cells during the cell cycle demonstrates continuity of localization. With the exception of the early G1 condition, the displayed cells are also displayed in Figure S11. Scale bars, 5 μm.