Figure 1.
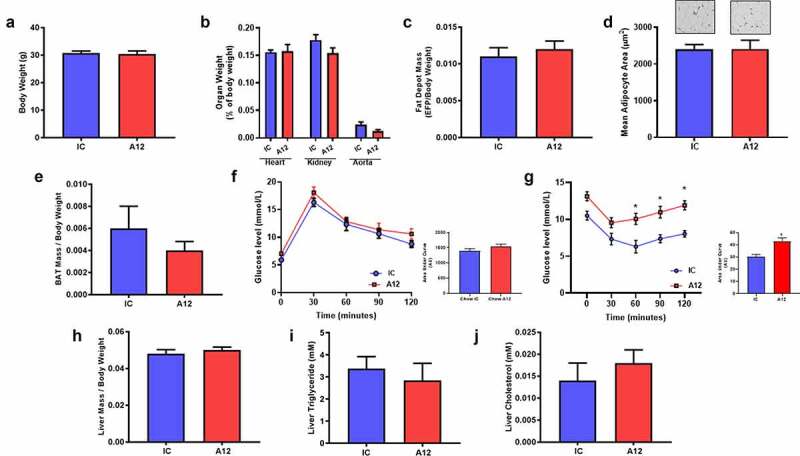
Examination of the effect of cixutumumab (A12) a specific antibody leading to internalization and degradation of the insulin like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1 R) in chow fed mice. Male C57BL/6 J mice were fed standard chow for 6 weeks and received 10 mg/kg cixutumumab or isotype control (IC) every 3 days by intraperitoneal injection for 3 weeks, 21 days after commencing diet. (a) No difference in body weight in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 5). (b) No difference in organ weight in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control treated mice (n = 26). (c) No difference in epididymal fat pad (EFP) weight in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control (n = 26). (d) No change in white adipocyte size in EFP from cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control (n = 12). (e) No change in brown adipose tissue (BAT) weight in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 18). (f) No difference in glucose tolerance tests in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 8). (g) Insulin tolerance tests in cixutumumab treated mice demonstrated a blunted decline in blood glucose in response to insulin compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 8). (h) No difference in liver weight in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 26). (i) No difference in hepatic triglyceride content in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 5). (j) No difference in hepatic cholesterol content in cixutumumab-treated mice compared to isotype control-treated mice (n = 5). Data expressed as mean (SEM),* denotes P < 0.05, n denotes number of mice per group, comparisons made using unpaired students t test or area under curve (AUC) where indicated.
