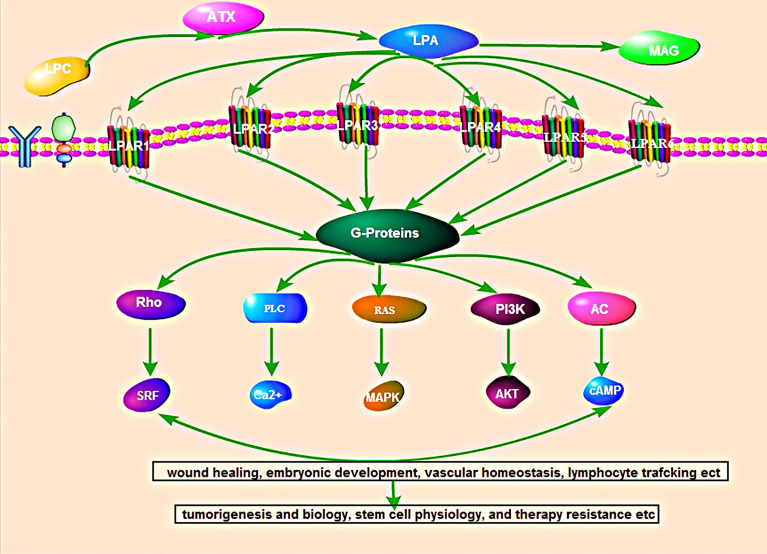
Figure 1.
Overview of the autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid signaling pathway. ATX produces the lipid mediator and GPCR agonist lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) from abundantly available extracellular lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). LPA signal through its six homologous receptors (LPAR1-6) that is binds to G proteins to activate downstream signaling pathways, including those involving Ras/Raf, RhoA, phosphoinositide 3-kinases, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin. The activated LPA-LPAR pathway participates in wound healing, embryonic development, vascular homeostasis, lymphocyte trafficking, cancer biology, stem cell physiology, and therapy resistance, etc.