Figure 6.
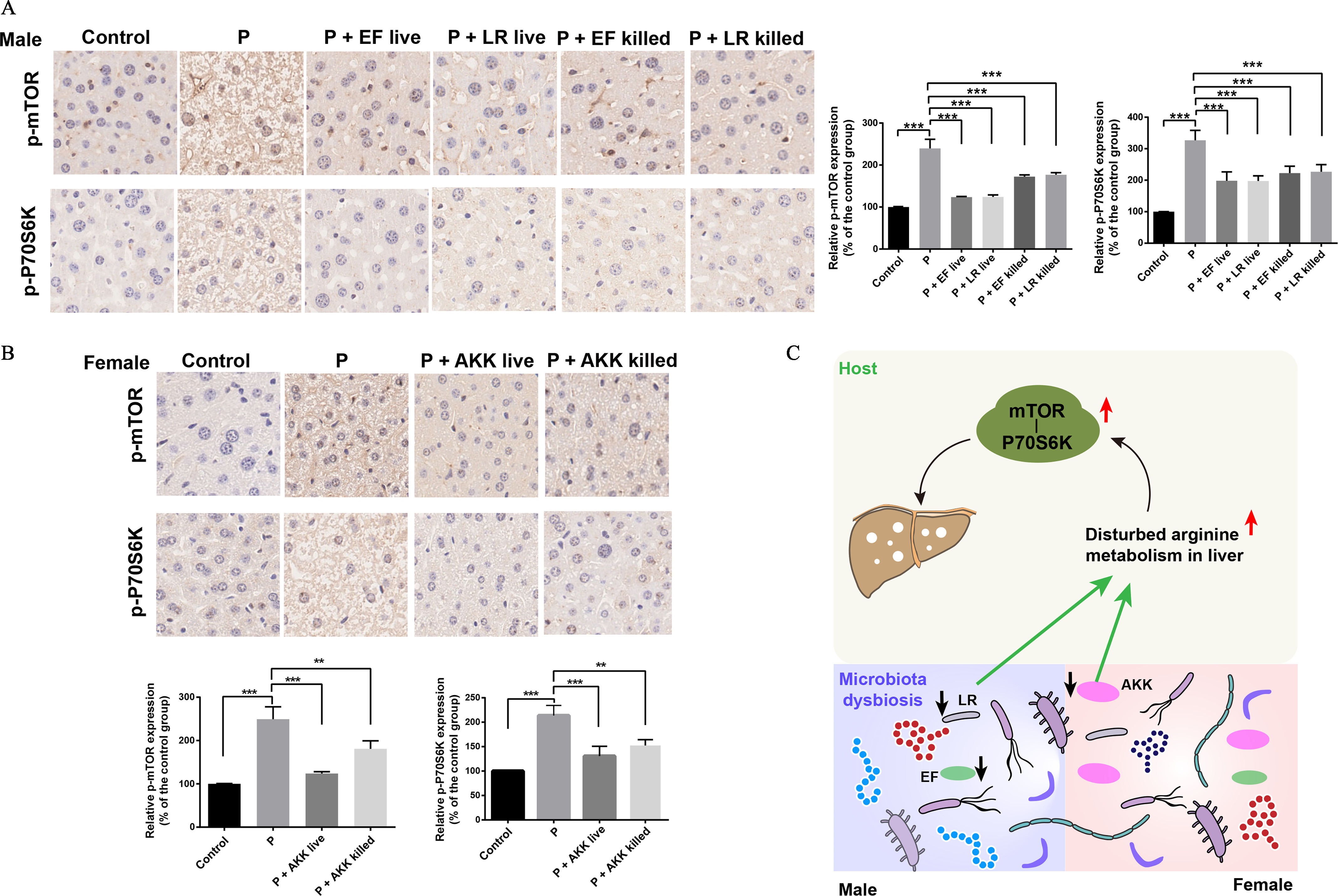
The effects of PFOS on the expressions of mTOR and P70S6K. (A) Expression of phosphorylated mTOR and P70S6K in fixed liver tissues of male mice in the indicated groups. (B) Expression of phosphorylated mTOR and P70S6K in fixed liver tissues of female mice in the indicated groups. (C) Schematic diagram of a potential mechanism by which the fecal microbiota contributes to PFOS-induced liver injury. PFOS regulates the abundances of fecal microbiota, which in turn contribute to the regulation of arginine levels in livers and then result in the activation of mTOR-P70S6K signaling pathway that can cause liver injury. , The relative intensity represents the ratio between the expression level of phosphorylated protein (p-mTOR and p-P70S6K) and the total protein expression level (mTOR and P70S6K). Summary data can be found in Table S7. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Results were presented as the . Note: AKK, Akk. muciniphila; ANOVA, analysis of variance; EF, E. faecalis; LR, L. reuteri; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; P and PFOS, perfluorooctane sulfonate; SD, standard deviation. *. **. *** in comparison with the indicated group.
