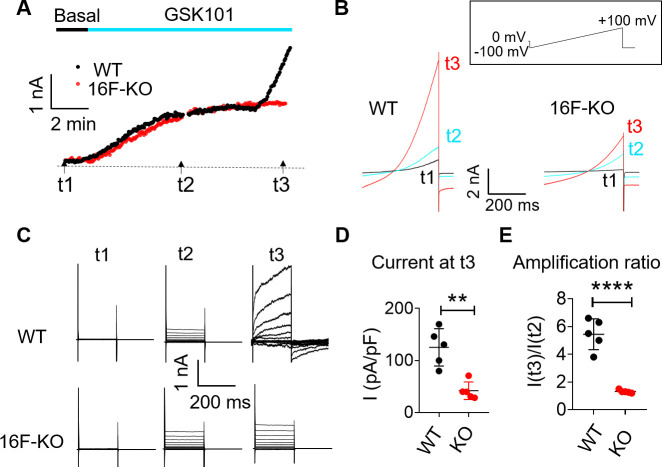
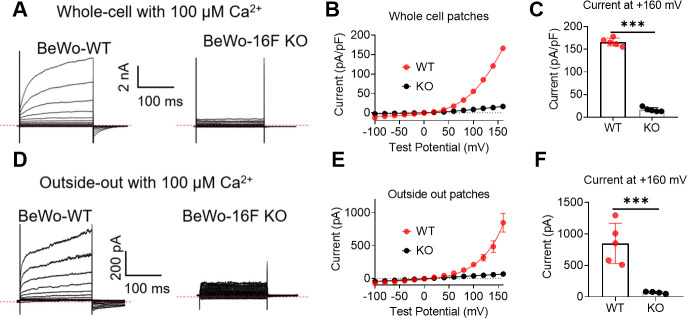
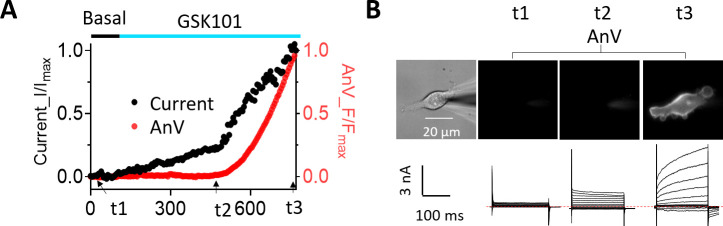
Figure 3. TRPV4 activation elicits TMEM16F current in BeWo cells.
(A, B) Time course of whole-cell currents in response to 30 nM GSK101 stimulation in WT and TMEM16F-KO BeWo cells. The currents were elicited with the ramp protocol shown in (B) (top). (A) The current amplitudes at +100 mV were plotted every 5 s. (B) Representative currents at three different time points as shown in (A). (C) Representative current traces elicited by a voltage step protocol (200 ms) from –100 to +140 mV at three different time points t1, t2, and t3 as indicated in (A). (D) Statistical analysis of current density (+100 mV) at t3 in WT and TMEM16F-KO BeWo cells. The current was elicited by the voltage steps shown in (C). Values represent mean ± SEM and statistics were done using Student’s t-test (n=5 for each group, **: p<0.01). (E) Statistical analysis of amplification ratio (current amplitude ratio at t3 and t2 in (C)) in WT and TMEM16F-KO BeWo cells. Values represent mean ± SEM and statistics were done using Student’s t-test (n=5 for each group, ****: p<0.0001). WT, wild-type.