Figure 1.
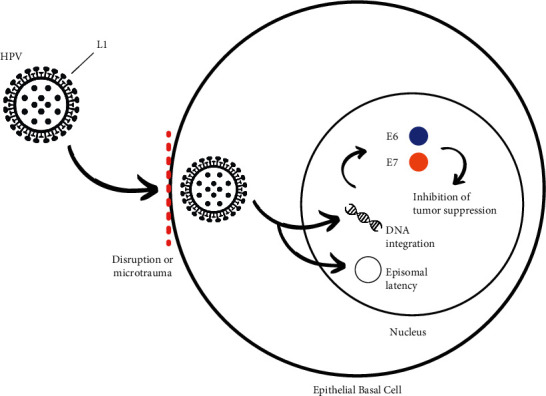
Mechanism of oral infection and carcinogenesis of HPV. In the presence of microtrauma of the basal epithelium of the host cell, HPV enters through interaction between the L1 proteins of its capsid and cell surface receptors. It is then incorporated into the cell nucleus where it can either remain in an episomal state or undergo DNA integration. E6 and E7 proteins inhibit tumor suppression.
