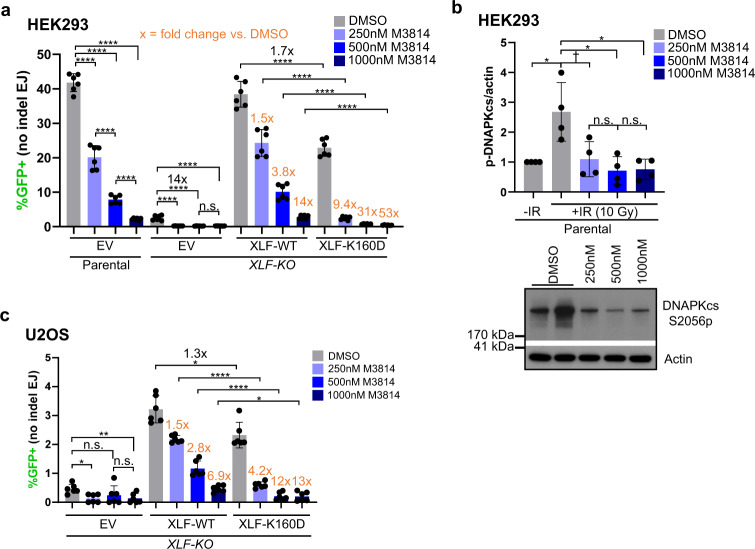
Fig. 2. Inhibiting DNAPKcs kinase activity suppresses No Indel EJ to a greater degree when combined with XLF-K160D.
a Effect of DNAPKcs kinase inhibitor M3814 on No Indel EJ in HEK293 cells with XLF-WT, XLF-K160D, and without XLF. Control cells treated with DMSO (the vehicle for M3814). n = 6 biologically independent transfections. Statistics with unpaired two-tailed t test using Holm–Sidak correction. ****P < 0.0001, n.s.= not significant. Fold-effects are shown to facilitate comparisons of the effect of each M3814 treatment on XLF-WT vs. K160D. b M3814 decreases ionizing radiation (IR)-induced phosphorylation of DNAPKcs at S2056 (S2056p). Shown are levels of DNAPKcs-S2056p normalized to Actin, and a representative immunoblot. n = 4 biologically independent wells of seeded cells. Statistics as in (a). DMSO −IR vs + IR *P = 0.0142, DMSO + IR vs. 500 nM M3814 + IR *P = 0.0497, DMSO + IR vs. 1000 nM M3814 + IR *P = 0.0497, DMSO + IR vs. 250 nM M3814 + IR †P = 0.0328 but not significant after correction (unadjusted P-value), n.s.= not significant. c The influence of DNAPKcs kinase inhibition with XLF-K160D is similar in U2OS cells. n = 6 biologically independent transfections. Statistics as in (a). ****P < 0.0001, EV DMSO vs. EV 1000 nM M3814 **P = 0.00311, EV DMSO vs. EV 250 nM M3814 *P = 0.0116, XLF-WT DMSO vs. XLF-K160D DMSO *P = 0.042, XLF-WT 1000 nM M3814 vs. XLF-K160D 1000 nM *P = 0.0169, n.s.= not significant. Data are represented as mean values ± SD.