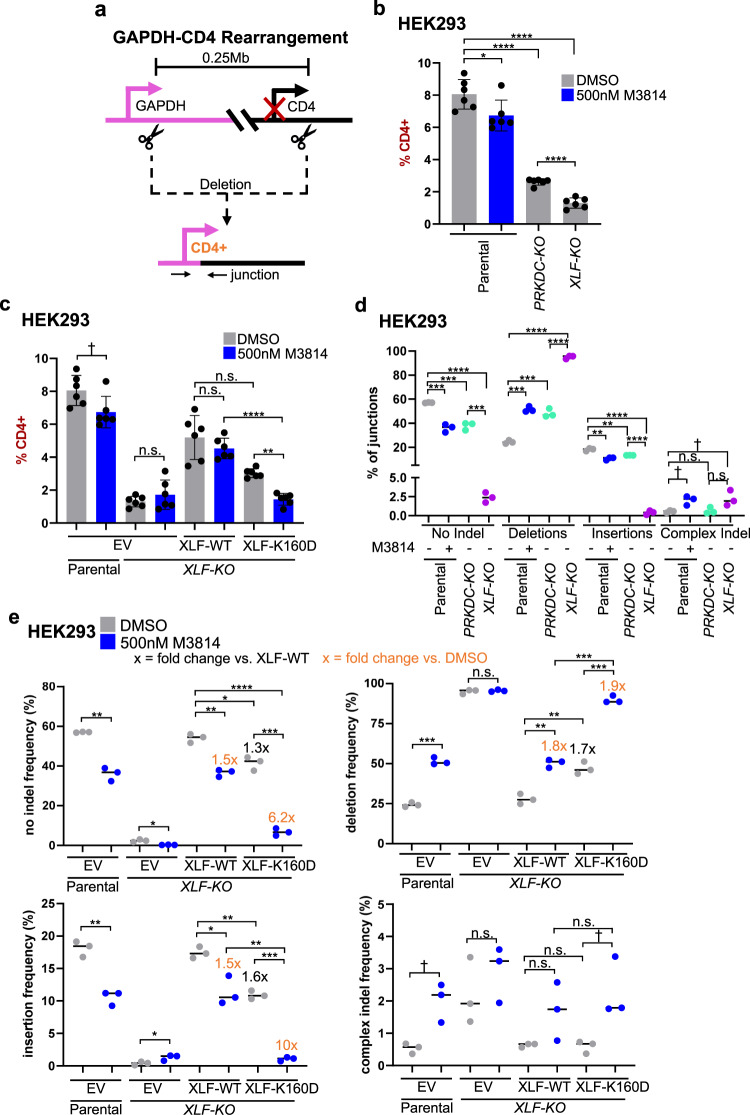
Fig. 3. Inhibiting DNAPKcs kinase activity affects EJ junction patterns to a greater degree when combined with XLF-K160D.
a Shown is the GAPDH-CD4 rearrangement assay, which uses the endogenous genes (not to scale). HEK293 cells are transfected with expression vectors for Cas9 and the two sgRNAs, with complementing vector(s) or empty vector (EV). CD4 frequencies are normalized to transfection efficiency with parallel GFP transfections. CD4+ cells are sorted using FACS and used to analyze the GAPDH-CD4 junction patterns by amplicon deep sequencing. b Loss of DNAPKcs and XLF leads to decreased CD4+ cells. HEK293 cells were treated with DMSO or 500 nM M3814. n = 6 biologically independent transfections. Statistics with unpaired two-tailed t test using Holm–Sidak correction. ****P < 0.0001, *P = 0.0349. c Combining 500 nM M3814 and XLF-K160D causes a decrease in CD4+ cells. n = 6 biologically independent transfections. Statistics as in (b). ****P < 0.0001, **P = 0.00128, †P = 0.0349 but not significant after correction (unadjusted P-value), n.s. not significant. d DNAPKcs is less important to promote No Indel EJ and insertions and suppress deletions compared to XLF. Shown are four types of EJ junctions from amplicon deep sequencing. n = 3 biologically independent transfections. Statistics as in (b). ****P < 0.0001, No Indel Parental DMSO vs. Parental 500 nM M3814 ***P = 0.00083, No Indel Parental DMSO vs. PRKDC-KO ***P = 0.00083, No Indel PRKDC-KO vs. XLF-KO ***P = 0.000141, Deletions Parental DMSO vs. Parental 500 nM M3814 ***P = 0.000113, Deletions Parental +DMSO vs. PRKDC-KO ***P = 0.000391, Insertions Parental DMSO vs Parental 500 nM M3814 **P = 0.00273, Insertions Parental DMSO vs. PRKDC-KO **P = 0.00273, Complex Indel Parental DMSO vs Parental 500 nM M3814 †P = 0.0149 but not significant after correction (unadjusted P-value)., Complex Indel Parental +DMSO vs XLF-KO †P = 0.0491 but not significant after correction (unadjusted P-value), n.s. not significant. e DNAPKcs kinase inhibition affects EJ junctions to a greater degree when combined with XLF-K160D. The frequency of the four types of EJ junctions in (d) are shown. n = 3 biologically independent transfections. Statistics as in (b). No Indel: ****P < 0.0001, ***P = 0.000481, Parental EV DMSO vs 500 nM M3814 **P = 0.00166, XLF-KO XLF-WT DMSO vs 500 nM M3814 **P = 0.00166, *P = 0.107. Deletions: Parental EV DMSO vs 500 nM M3814 ***P = 0.000284, XLF-KO XLF-WT 500 nM M3814 vs. XLF-K160D 500 nM M3814 ***P = 0.000228, XLF-KO XLF-K160D DMSO vs. 500 nM M3814 ***P = 0.000312. Insertions: ***P = 0.000106, Parental EV DMSO vs. 500 nM M3814 **P = 0.00564, XLF-KO XLF-WT DMSO vs. XLF-K160D DMSO **P = 0.00245, XLF-KO XLF-WT 500 nM M3814 vs. XLF-K160D 500 nM M3814 **P = 0.00516, *P = 0.023. Complex Indel: Parental EV DMSO vs. 500 nM M3814 †P = 0.0149 but not significant after correction (unadjusted P-value), XLF-KO XLF-K160D DMSO vs. 500 nM M3814 †P = 0.0346 but not significant after correction (unadjusted P-value). Data are represented as mean values ± SD.