Figure 2.
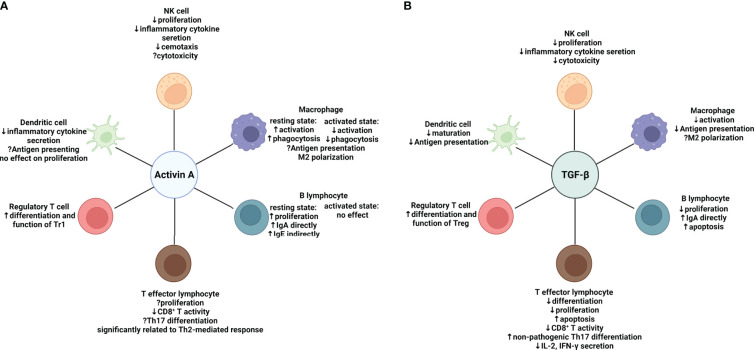
Effects of activin A and TGF-β on major components of both the innate and adaptive immune system respectively. (A) Effects of Activin A on the immune system: in regulation of the innate immune system, activin A suppresses proliferation, inflammatory cytokine secretion and chemotaxis of NK cells, while effects on cytotoxicity remain uncertain. The effects of activin A on macrophages depend on the activation state. Activin A promotes activation and phagocytosis of resting macrophages while suppressing that of macrophages in an activation state. Despite the elusive function in antigen-presenting, activin A seems to skew macrophages toward M2 type. Meanwhile, activin A shows inhibition of secretion of a variety of cytokines by activated DC cells. In regulation of the adaptive immune system, activin A directly induces proliferation and IgA production of resting B cells without affecting activated B cells. It can also induce IgE production indirectly by means of other immune cells in vivo. Activin A is significantly related to Th2-mediated response and suppressive in CD8+ T activity. Its role in Th17 differentiation remains controversial. In contrast to TGF-β, activin A may be inclined to induce the differentiation of IL-10-producing Tr1s. (B) Effects of TGF-β on the immune system. In regulation of innate immune system, TGF-β exert similar effects on NK cells to activin A It suppresses activation and antigen presentation of macrophages. More evidence is needed to prove it can induce M2-like polarization. TGF-β also inhibits maturation and antigen presentation of DCs. In regulation of adaptive immune system, TGF-β shows a wide range of immune suppressive effects. It suppresses the survival of both B and T cells. In line with activin A, it can induce IgA production by B cells and suppress CD8+ T activity. However, it favors differentiation of non-pathogenic Th17 and Foxp3+ Tregs. Suppressive effect (downward arrow); promoting effect (upward arrow); uncertain effect (question mark); NK cell, natural killer cell. Created with BioRender.com.