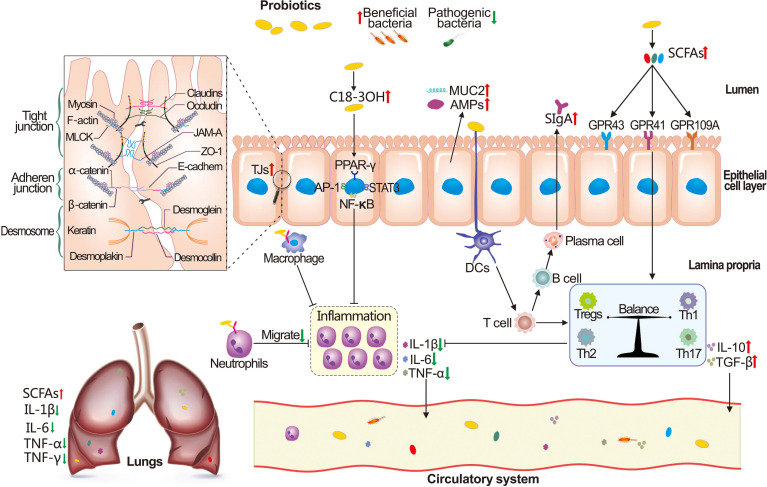
Figure 6.
Possible mechanisms of probiotics supplementation on PALI recovery. Probiotics can restore the function of the intestinal barrier by inhibiting the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, increasing the production of 3-hydroxyoctadecenoic acid (C18-3OH), short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), mucin2 (MUC2), and secretory IgA (SIgA), and regulating the expression of tight junction (TJ) proteins. In addition, probiotics have the capacity to reduce the neutrophil infiltration and release of inflammatory cytokines, maintain the balance of the intestinal immune system, and reduce the translocation of bacteria, inflammatory factors, etc., resulting in the alleviation of PALI.