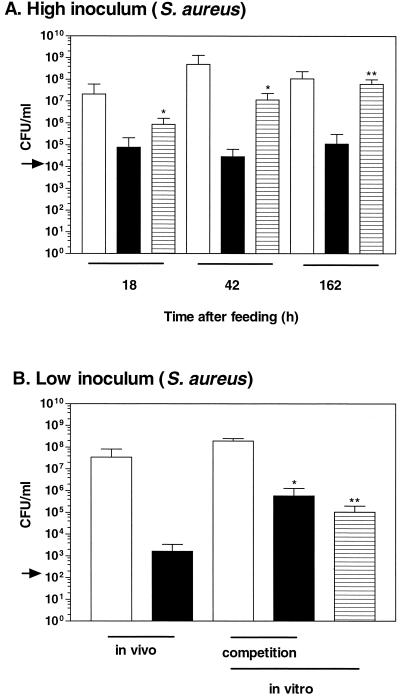
FIG. 3.
Colonization of H. medicinalis by S. aureus. (A) High inoculum. The S. aureus strain was unable to replicate as well inside the animal as in the in vitro control. The extent of the colonization by SaR1, an Rifr S. aureus strain, was assessed 18, 42, or 162 h after inoculation. The blood was fed to the animal or incubated in vitro. The arrow depicts the concentration of SaR1 in the inoculum. The concentration of the bacteria recovered from the intraluminal fluid of the digestive tract was determined (native flora and SaR1 recovered on blood agar [open bar] and SaR1 recovered on LB-RIF plates [solid bar]). The concentration of SaR1 recovered from the in vitro blood control is depicted with a hatched bar. (B) Low Inoculum after 18 h of incubation. SaR1 was fed to the animal and incubated in vitro either alone or in competition with a symbiotic strain that was sensitive to RIF. For the competition experiment, the concentration of A. veronii strain and SaR1 recovered on blood agar is represented with an open bar and that of SaR1 recovered on LB-RIF plates is represented with a solid bar. ∗ and ∗∗, the mean concentrations differed significantly from the mean concentrations obtained in vivo at P < 0.05 and P < 0.005, respectively.