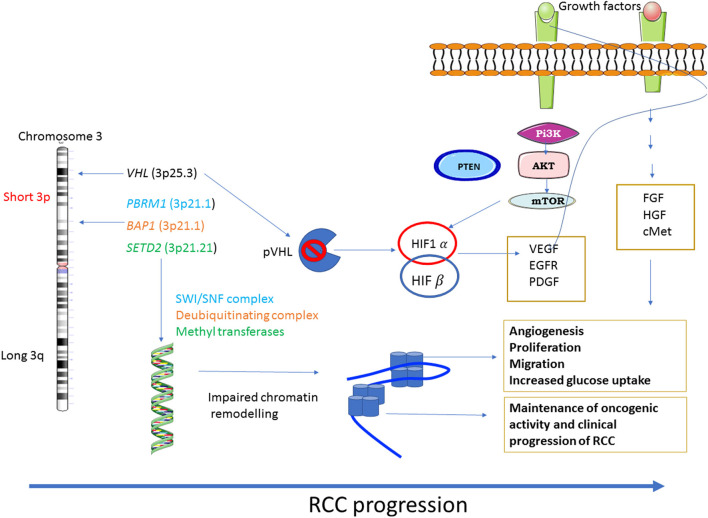
Figure 1.
Major dysregulated pathways in RCC: RCC shows a diverse range of genetic mutations. Loss of chromosome 3p tumor suppressor genes play a major role in the pathogenesis of RCC. Genes mostly affected are VHL, the gene responsible for sensing oxygen levels within a cell, chromatin remodeling genes such as PBRM1, BAP1 and SETD2. The other signaling pathways that are associated with RCC progression are PI3K-AKT-mTOR and the pathways regulated by FGF, HGF and its receptor c-MET.