Fig. 5.
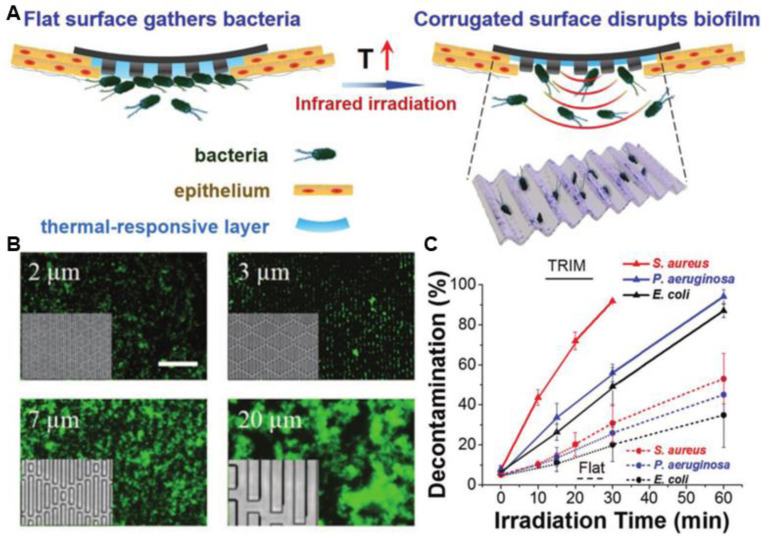
The topical thermal ablation of the TRIM films. (A) TRIM films with flat surface normally while reproducing corrugated microtopography during heating (via infrared-light irradiation). The corrugated surface would induce thermally activated disruption of the biofilm and facilitate the ablation of planktonic bacteria, while mitigating the thermal harm to host epithelium. (B) Fluorescence images show that S. aureus (green) attached within feature gaps when dispersed on films with different features. On surfaces with 5 µm and larger features, S. aureus formed aggregates. Inset: PDMS film with varied features. Scale bar: 50 µm. (C) Antibacterial efficiency of TRIM films or flat film. Reproduced from [60] with permission from WILEY-VCH. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)