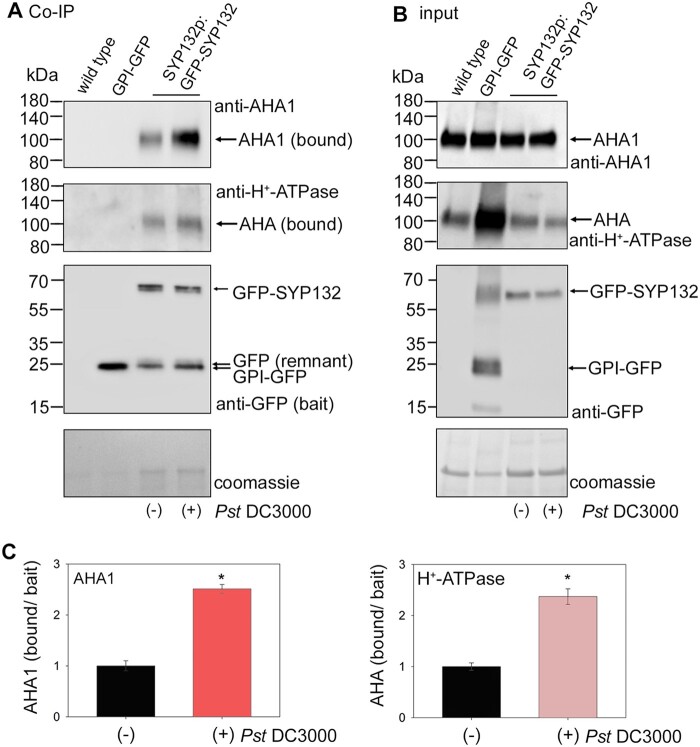
Figure 5.
Bacterial infection influences SYP132 co-immunoprecipitant AHA1 levels. A, Immunoblots (representative) showing Co-IP assays using leaf lysates from wild-type, CaMV 35S: GPI-GFP or SYP132p:GFP-SYP132 Arabidopsis. SYP132p:GFP-SYP132 plants were treated over 24 h without (−) or with (+) Pseudomonas syringae (Pst DC3000) inoculum in 10 mM MgCl2 before lysis of leaf tissue. Input lysates were adjusted for equal GFP-tagged bait loads. Lysates were added in excess to saturate bait binding on the GFP-trap columns. Note therefore that input and bound GFP-SYP132 are similar in each case. Co-immunoprecipitants were eluted following washes to remove loosely bound proteins. Images are (top to bottom panels), immunoblots detecting AHA1 (bound) using anti-AHA1 antibodies at ∼100 kDa, all isoforms of AHA (bound) using anti-H+-ATPase antibodies at ∼100 kDa, baits GPI-GFP at ∼24 kDa or GFP-SYP132 at ∼62 kDa using anti-GFP antibodies and total protein per lane detected using Coomassie stain. Nonspecific AHA1 or AHA binding to the GFP-trap incubated with wild-type Arabidopsis lysate lacking GFP or with GFP-trap bound to GPI-GFP derived from 35S: GPI-GFP Arabidopsis lysates as bait was not observed, serving as experimental controls. A remnant protein at ∼24 kDa was detected using anti-GFP antibodies in the Co-IP in addition to GFP-SYP132. B, Images are (top to bottom panels), immunoblots of leaf lysates (inputs) used in the Co-IP detecting AHA1 protein using anti-AHA1 antibodies, all isoforms of AHA at ∼100 kDa using anti-H+-ATPase antibodies, GPI-GFP at ~24 kDa or GFP-SYP132 at ∼62 kDa using anti-SYP132 antibodies, and total protein per lane stained using Coomassie. C Mean ± se of AHA1 (left panel) and PM H+-ATPase (right panel) proteins bound in the Co-IP normalized to GFP-SYP132 bait. Graphs show Co-IP bound/bait following Pst DC3000 infection, relative to control. Data are means ± se and “*” denote statistically significant differences determined using t test (P < 0.001). Experiments used ≥5 plants for each, N = 3.