FIG. 1.
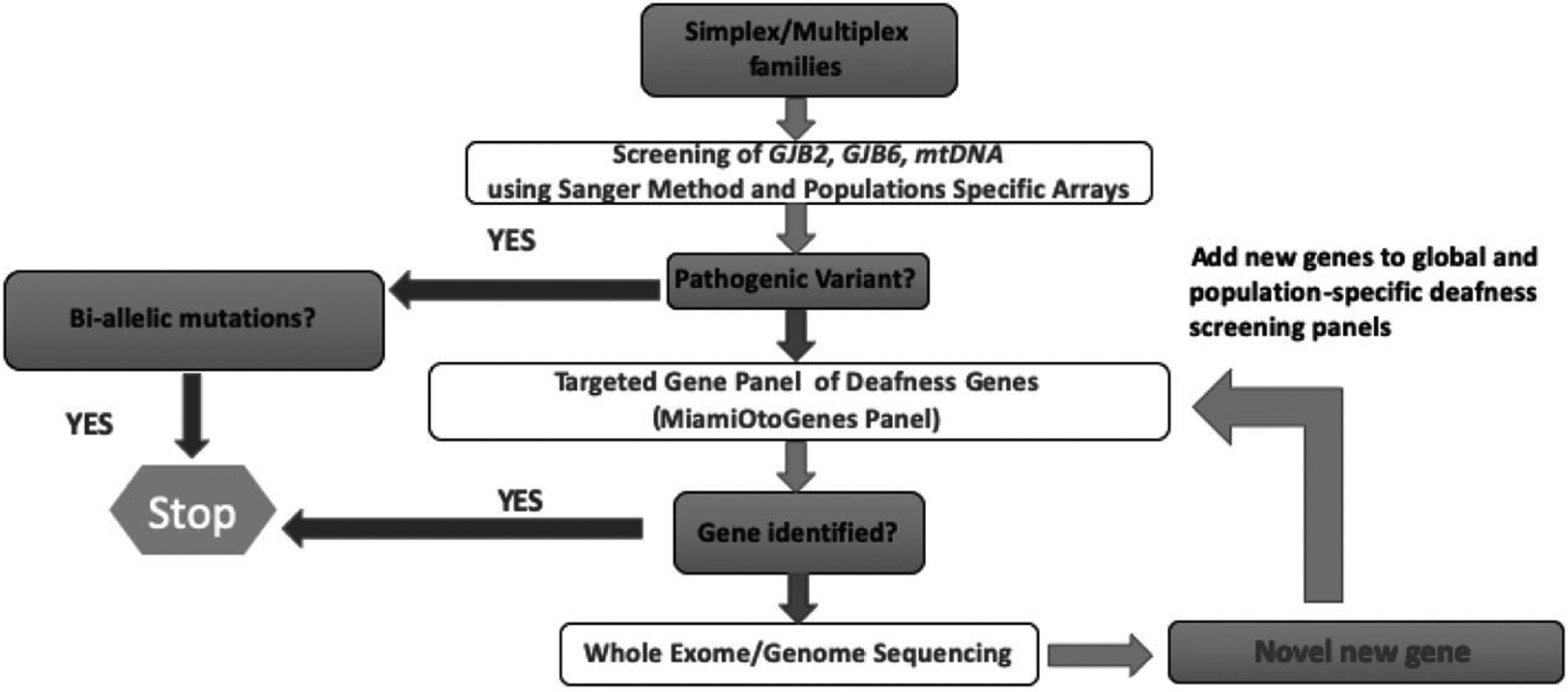
Population-based genetic workflow for mutational analysis for clinical nonsyndromic SNHL profiling. To detect nonsyndromic SNHL mutations, patients are initially screened for population-specific pathogenic variants in GJB2, GJB6, and mtDNA. If biallelic pathogenic variants are not identified, patients are screened with a global or population-specific gene panel. If a causative mutation cannot be determined, then whole exome sequencing (WES) or whole genome sequencing (WGS) is performed, and if a novel gene is discovered it is added to the appropriate panel for future screening. SNHL indicates sensorineural hearing loss.
